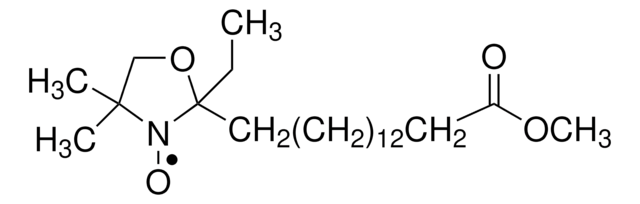253596
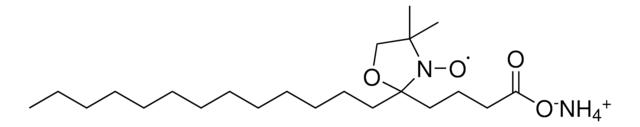
16-DOXYL-stearic acid, free radical
Sinónimos:
16-SASL, 16DOXYL, 16NS, 2-(14-Carboxytetradecyl)-2-ethyl-4,4-dimethyl-3-oxazolidinyloxy, free radical
About This Item
Productos recomendados
formulario
solid
Nivel de calidad
mp
47-55 °C (lit.)
grupo funcional
carboxylic acid
ether
temp. de almacenamiento
2-8°C
cadena SMILES
CCC1(CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O)OCC(C)(C)N1[O]
InChI
1S/C22H42NO4/c1-4-22(23(26)21(2,3)19-27-22)18-16-14-12-10-8-6-5-7-9-11-13-15-17-20(24)25/h4-19H2,1-3H3,(H,24,25)
Clave InChI
RPAZYIOIDZRJOO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Aplicación
- Dynamics and state of lipid bilayer-internal water using 1H dynamic nuclear polarization
- Distribution of fatty acids
- Transversal relaxation of nitroxides for PELDOR Spectroscopy
- Effects of different lipid components on detergent-resistant membranes
Código de clase de almacenamiento
11 - Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
235.4 °F - closed cup
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
113 °C - closed cup
Equipo de protección personal
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico