676802
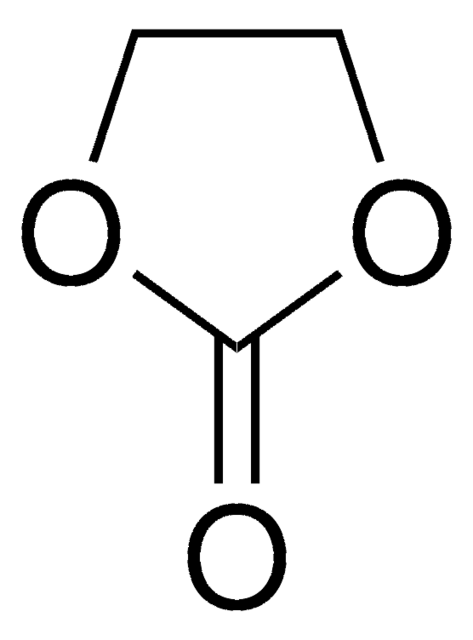
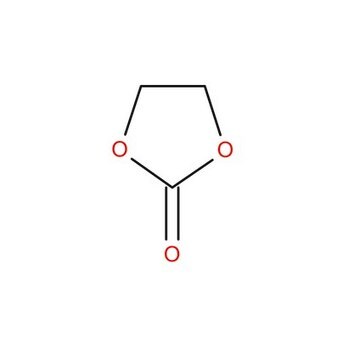
Ethylene carbonate
anhydrous, 99%
Synonym(s):
1,3-Dioxolan-2-one
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
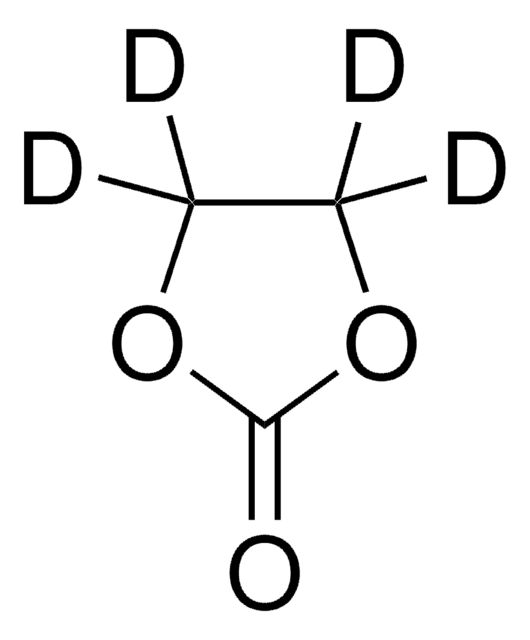
C3H4O3
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
88.06
Beilstein:
106249
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
Recommended Products
grade
anhydrous
Quality Level
vapor density
3.04 (vs air)
vapor pressure
0.02 mmHg ( 36.4 °C)
Assay
99%
form
solid
expl. lim.
3.6-16.1 % (lit.)
impurities
≤0.006% water
bp
243-244 °C/740 mmHg (lit.)
mp
35-38 °C (lit.)
density
1.321 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
O=C1OCCO1
InChI
1S/C3H4O3/c4-3-5-1-2-6-3/h1-2H2
InChI key
KMTRUDSVKNLOMY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Ethylene carbonate is a cyclic carbonate with high dielectric constant.
Application
Applications of ethylene carbonate (EC):
- EC can be an effective liquefying reagent for cellulose liquefaction.
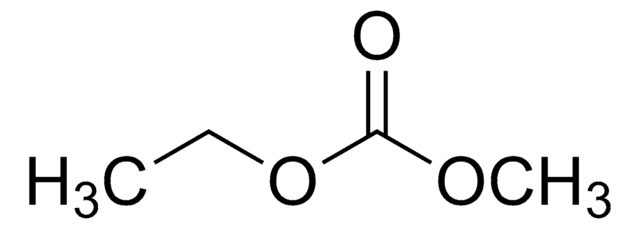
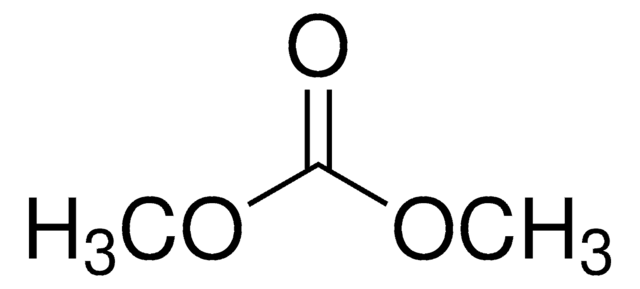
- Dimethyl carbonate (DMC) can be synthesized via the transesterification of EC and methanol.
- EC can be a non-hazardous alternative to phosgene and isocyanates for the synthesis of polyurethanes.
related product
Product No.
Description
Pricing
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Irrit. 2 - STOT RE 2 Oral
Target Organs
Kidney
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
289.4 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
143 °C - closed cup
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Rapid liquefaction of lignocellulosic waste by using ethylene carbonate.
Yamada T and Ono H
Bioresource Technology, 70(1), 61-67 (1999)
Transesterification of urea and ethylene glycol to ethylene carbonate as an important step for urea based dimethyl carbonate synthesis.
Bhanage B M, et al.
Green Chemistry, 5(4), 429-432 (2003)
Synthesis of oligocarbonate diols from ethylene carbonate and aliphatic diols catalyzed by alkali metal salts.
Pawlowski P and Rokicki G
Polymer, 45(10), 3125-3137 (2004)
Mehran Ghasemlou et al.
Carbohydrate polymers, 246, 116656-116656 (2020-08-05)
Manufacturing of multifunctional materials through blending is a promising route for improving performance of biopolymers including starch. Non-isocyanate polyurethanes (NIPUs) are an emerging group of green materials. Understanding the mechanism of interaction between starch and NIPU not only highlights underlying
Dielectric properties and relaxation in ethylene carbonate and propylene carbonate.
Payne R and Theodorou IE.
The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 76(20), 2892-2900 (1972)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service