I2512
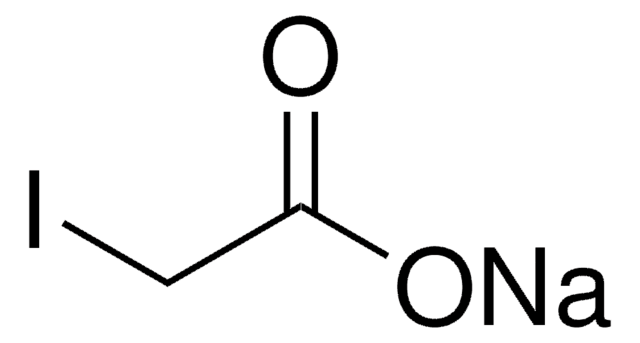
Sodium iodoacetate
powder, ≥98%
Synonym(s):
Iodoacetic acid sodium salt
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
ICH2COONa
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
207.93
Beilstein:
4009322
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352202
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.77
Recommended Products
Product Name
Sodium iodoacetate, ≥98%
biological source
synthetic (organic)
Assay
≥98%
form
powder
mp
208 °C (dec.) (lit.)
solubility
H2O: 100 mg/mL
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
[Na+].[O-]C(=O)CI
InChI
1S/C2H3IO2.Na/c3-1-2(4)5;/h1H2,(H,4,5);/q;+1/p-1
InChI key
AGDSCTQQXMDDCV-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
Reagent for the modification of cysteine residues in proteins.
Reagent for the modification of cysteine residues in proteins. Used in protein sequencing (including by Sanger in sequencing bovine insulin) to prevent oxidation of -SH sidechains.
Reagent for the modification of cysteine residues in proteins. Used to induce animal osteoarthritis model system, which mimics both symptoms and histopathology of the human disease.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Used to induce osteoarthritis-like lesions and functional impairment in rats, for testing of chondroprotective agents and diagnostic imaging techniques.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B
Storage Class Code
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
406.4 °F
Flash Point(C)
208 °C
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
C Guingamp et al.
Arthritis and rheumatism, 40(9), 1670-1679 (1997-10-27)
To characterize the dose-responsiveness of morphologic and biochemical chondral changes relative to mobility in mono-iodoacetate (MIA)-induced osteoarthritis (OA) in rats. Rat mobility was assessed by biotelemetry. Articular lesions were characterized by macroscopic and histologic examinations. Cartilage proteoglycan metabolism was evaluated
Roberto E Guzman et al.
Toxicologic pathology, 31(6), 619-624 (2003-10-31)
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease characterized by joint pain and a progressive loss of articular cartilage. Studies to elucidate the pathophysiology of OA have been hampered by the lack of a rapid, reproducible animal model that mimics both
Matilde Tschon et al.
Cells, 9(7) (2020-07-02)
The purpose of this study was to verify the efficacy of a single intra-articular (i.a.) injection of a hyaluronic acid-chitlac (HY-CTL) enriched with two low dosages of triamcinolone acetonide (TA, 2.0 mg/mL and 4.5 mg/mL), in comparison with HY-CTL alone
Ikufumi Takahashi et al.
PloS one, 13(4), e0196625-e0196625 (2018-04-27)
This study aimed to investigate the histopathological changes in the patellofemoral joint using a rat model of osteoarthritis that was induced using monosodium iodoacetate, and to establish a novel model of patellofemoral osteoarthritis in a rat model using histopathological analysis.
Hyung Jin Lim et al.
Food science & nutrition, 8(12), 6550-6556 (2020-12-15)
In Asia, Vigna angularis (azuki bean) has been used as a traditional medicine to treat various diseases because of its biological properties. Osteoarthritis (OA) and osteoporosis (OP) are common regenerative bone diseases that are characterized by deterioration of joint and
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service