913901
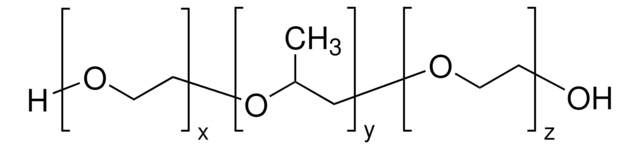
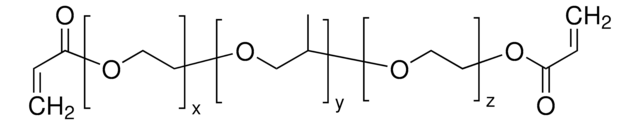
Poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(propylene glycol)-block-poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate
average Mn ~14,600
Synonym(s):
F-108 dimethacrylate, PEG-PPG-PEG, Pluronic dimethacrylate
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
C4H5O[C2H4O]x[C3H6O]y[C2H4O]zC4H5O2
UNSPSC Code:
12162002
NACRES:
NA.23
Recommended Products
form
powder
Quality Level
mol wt
average Mn ~14,600
contains
≤1500 ppm MeHQ
color
off-white to yellow
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
Poloxamers are nonionic, triblock copolymers containg a central hydrophobic chain of poly(propylene glycol) (PPG) and two terminal hydrophilic chains of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG). Due to their amphiphilic structure, poloxamer solutions feature temperature dependent self-assembling and thermo-gelling behavior. Concentrated aqueous solutions of poloxamers are liquid at low temperature and form a gel at higher temperature, in a reversible process. This characteristic has allowed for these materials to be used as drug carriers for most routes of administration including oral, topical, intranasal, ocular, and parenteral. Methacrylate-modified derivatives are most commonly used as thermosensitive hydrogels for drug delivery and 3D bioprinting applications. After casting or printing, the material can be crosslinked to preserve the hydrogel structure.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
High-Throughput Printing via Microvascular Multinozzle Arrays.
Hansen C J, et al.
Advanced Materials, 25(1), 96-10 (2013)
Application of thermoreversible pluoronic F-127 gels in Pharmaceutical formulations.
Escobar-Chavez J J, et al.
J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci., 9(3), 339-358 (2006)
Self-Assembly of Pluronic F127 Diacrylate in Ethylammonium Nitrate: Structure, Rheology, and Ionic Conductivity before and after Photo-Cross-Linking.
Lopez Barron C R, et al.
Macromolecules, 49(14), 5179-5189 (2016)
Smart hydrogels for 3D bioprinting.
Wang S, et al.
International Journal of Bioprinting, 1(1), 3-14 (2015)
Michael Müller et al.
Biofabrication, 7(3), 035006-035006 (2015-08-12)
Bioprinting is an emerging technology in the field of tissue engineering as it allows the precise positioning of biologically relevant materials in 3D, which more resembles the native tissue in our body than current homogenous, bulk approaches. There is however
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service