Alle Fotos(1)
Wichtige Dokumente
N5661
Nuklease S1 aus Aspergillus oryzae
for single-strand DNA/RNA digestion
Synonym(e):
Endonuclease S1
Anmeldenzur Ansicht organisationsspezifischer und vertraglich vereinbarter Preise
Alle Fotos(1)
About This Item
CAS-Nummer:
MDL-Nummer:
UNSPSC-Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.54
Empfohlene Produkte
Biologische Quelle
Aspergillus sp. (A. oryzae)
Form
solution
Konzentration
≥100000 units/mL
Methode(n)
DNA purification: suitable
Eignung
suitable for nucleic acid purification
Anwendung(en)
cell analysis
Versandbedingung
wet ice
Lagertemp.
−20°C
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Verwandte Kategorien
Allgemeine Beschreibung
The Nuclease S1 enzyme from Aspergillus oryzae has the ability to degrade single-stranded oligonucleotides composed of either deoxynucleotides or ribonucleotides.
Anwendung
Nuclease S1 from Aspergillus oryzae has been used in a study to assess a biochemical method for mapping mutational alterations in DNA. It has also been used in a study to investigate the DNA damage and repair in a γ-irradiated rat brain tumor.
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
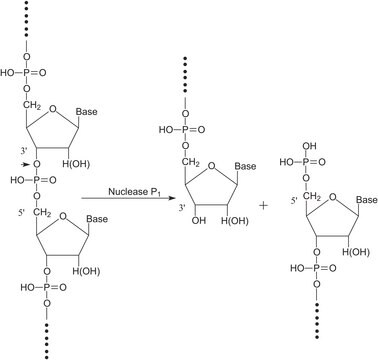
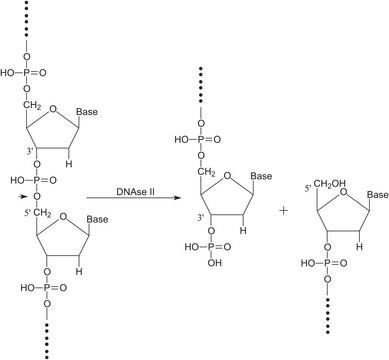
Nuclease S1 isolated from Aspergillus oryzae exhibits endo- and exolytic hydrolytic activity for the phosphodiester bonds of single-stranded DNA and RNA yielding 5′-phosphomononucleotide and 5′-phosphooligonucleotide end-products. It is used to digest non-annealed polynucleotide tails and hairpin loops in RNA and DNA duplexes and can be used to convert superhelical DNA to the linear form.
SI nuclease from Aspergillus oryzae can generate double-stranded DNA breaks in response to DNA nicks or abasic sites.
Einheitendefinition
One unit will cause 1.0 microgram of single-stranded nucleic acid to become perchloric acid soluble per minute at pH 4.6 at 37°C.
Physikalische Form
Lösung enthält 30 mM Natriumacetat, 50 mM NaCl, 1 mM ZnCl2, 50% Glycerin, 2 mg/ml Protein
Nur Kit-Komponenten
Produkt-Nr.
Beschreibung
- 30mM Sodium acetate .25-.25 %
- 50mM Sodium chloride .29 %
- 1mM Zinc chloride .01 %
- Glycerol 50 %
- 2mg/mL Protein .2 %
Lagerklassenschlüssel
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
F Harada et al.
Nucleic acids research, 2(6), 865-871 (1975-06-01)
Nuclease S1 specifically hydrolizes tRNAs in their anticodon loops, forming new 5' phosphate and 3' OH ends. Some single-stranded regions are not cut by nuclease S1. The strong preference of nuclease S1 for the anticodon region can be used for
M A Chaudhry et al.
Nucleic acids research, 23(19), 3805-3809 (1995-10-11)
Defined DNA substrates containing discrete abasic sites or paired abasic sites set 1, 3, 5 and 7 bases apart on opposite strands were constructed to examine the reactivity of S1, mung bean and P1 nucleases towards abasic sites. None of
P Beard et al.
Journal of virology, 12(6), 1303-1313 (1973-12-01)
S(1) nuclease, the single-strand specific nuclease from Aspergillus oryzae can cleave both strands of circular covalently closed, superhelical simian virus 40 (SV40) DNA to generate unit length linear duplex molecules with intact single strands. But circular, covalently closed, nonsuperhelical DNA
T E Shenk et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 72(3), 989-993 (1975-03-01)
S1 nuclease (EC 3.1.4.X), a single-strand-specific nuclease, can be used to accurately map the location of mutational alterations in simian virus 40 (SV40) DNA. Deletions of between 32 and 190 base pairs, which are at or below the limit of
S1 nuclease from Aspergillus oryzae for the detection of DNA damage and repair in the gamma-irradiated intracerebral rat gliosarcoma 9L.
P H Gutin et al.
Radiation research, 72(1), 100-106 (1977-10-01)
Protokolle
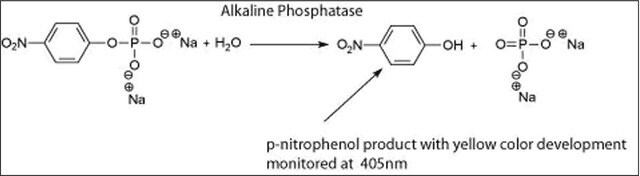
Enzymatic Assay of Nuclease S1
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.