Wichtige Dokumente
F1506
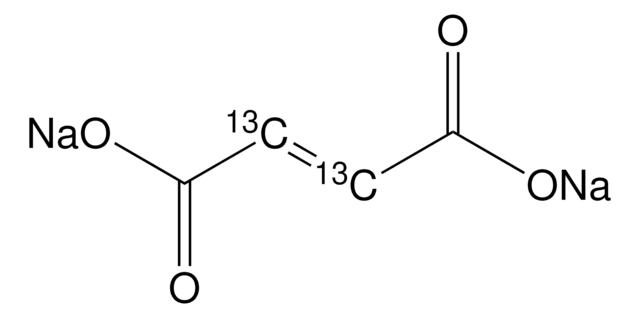
Natrium-fumarat dibasisch
≥99%
Synonym(e):
Dinatrium-fumarat, Fumarsäure Dinatriumsalz
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualitätsniveau
Assay
≥99%
SMILES String
[Na+].[Na+].[O-]C(=O)\C=C\C([O-])=O
InChI
1S/C4H4O4.2Na/c5-3(6)1-2-4(7)8;;/h1-2H,(H,5,6)(H,7,8);;/q;2*+1/p-2/b2-1+;;
InChIKey
MSJMDZAOKORVFC-SEPHDYHBSA-L
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Anwendung
- Enhancement of drug absorption: Sodium fumarate dibasic is utilized to improve the dissolution behavior and oral absorption of drugs with pH-dependent solubility, enhancing bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy in pharmaceutical applications (Salehi et al., 2021).
- Development of novel drug carriers: The compound is used in the synthesis and characterization of novel injectable drug carriers, aiming to enhance the delivery and efficacy of therapeutic agents in medical treatment strategies (Guo et al., 2005).
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Artikel
Learn about the four membrane-bound protein complexes that make up the electron transport chain metabolic pathway supplying energy as ATP for cellular respiration.
Information on fatty acid synthesis and metabolism in cancer cells. Learn how proliferatively active cells require fatty acids for functions such as membrane generation, protein modification, and bioenergetic requirements. These fatty acids are derived either from dietary sources or are synthesized by the cell.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.