C1700000
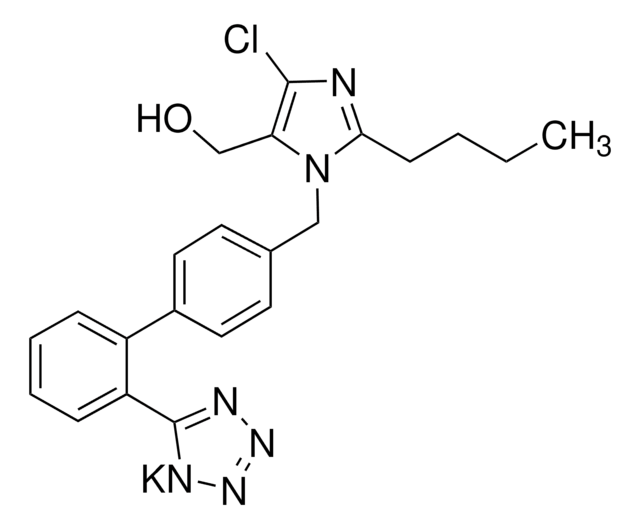
Chlorothiazid
European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard
Synonym(e):
6-Chlor-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazin-7-sulfonamid-1,1-dioxid
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualität
pharmaceutical primary standard
API-Familie
chlorothiazide
Hersteller/Markenname
EDQM
Anwendung(en)
pharmaceutical (small molecule)
Format
neat
SMILES String
O=S(C1=C2C=C(Cl)C(S(N)(=O)=O)=C1)(NC=N2)=O
InChI
1S/C7H6ClN3O4S2/c8-4-1-5-7(2-6(4)16(9,12)13)17(14,15)11-3-10-5/h1-3H,(H,10,11)(H2,9,12,13)
InChIKey
JBMKAUGHUNFTOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Angaben zum Gen
human ... SLC12A3(6559)
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Weitere Informationen und Unterstützung finden Sie auf der Webseite der entsprechenden Pharmakopöe.
Anwendung
Verpackung
Sonstige Hinweise
Ähnliches Produkt
Signalwort
Danger
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Sens. 1
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 2
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Kundensupport
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.