Wichtige Dokumente
36650
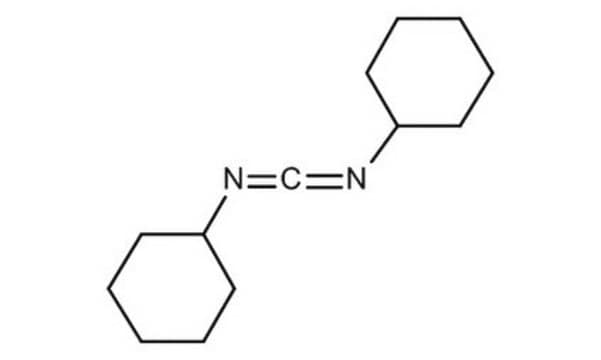
N,N′-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimid
≥99.0% (GC), for peptide synthesis
Synonym(e):
DCC
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Produktbezeichnung
N,N′-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimid, puriss., ≥99.0% (GC)
Qualität
puriss.
Qualitätsniveau
Assay
≥99.0% (GC)
Form
solid
Eignung der Reaktion
reaction type: Coupling Reactions
bp
122-124 °C/6 mmHg (lit.)
mp (Schmelzpunkt)
32.0-37.0 °C
34-35 °C (lit.)
Löslichkeit
methylene chloride: 0.1 g/mL, clear, colorless
Anwendung(en)
peptide synthesis
SMILES String
C1CCC(CC1)N=C=NC2CCCCC2
InChI
1S/C13H22N2/c1-3-7-12(8-4-1)14-11-15-13-9-5-2-6-10-13/h12-13H,1-10H2
InChIKey
QOSSAOTZNIDXMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Angaben zum Gen
human ... EPHX2(2053)
mouse ... Ephx2(13850)
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
It may be also used to synthesize:
- 1,3-Thiazetedine derivatives via [2+2] cycloaddition with 2-phenylethenyl- and 2-(4-nitrophenyl)ethenyl isothiocyanates.
- 1,3,5-Oxadiazine-4-thiones via [4+2] cycloaddition with benzoyl isothiocyanates.
- Sterically hindered 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives by reacting with (N-isocyanimino)triphenylphosphorane the presence of aromatic (or heteroaromatic) carboxylic acids.
Sonstige Hinweise
Signalwort
Danger
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Sens. 1
Lagerklassenschlüssel
6.1D - Non-combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic hazardous materials or hazardous materials causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
235.4 °F - closed cup
Flammpunkt (°C)
113 °C - closed cup
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Artikel
In principle, the seemingly simple formation of a peptide bond can be accomplished using all the procedures available in organic chemistry for the synthesis of carboxylic acid amides. However, due to the presence of various functional groups in natural and unnatural amino acids and particularly the requirement for full retention of chiral integrity, the coupling of amino acids and peptides under mild conditions can be challenging. A plethora of coupling reagents has been developed superseding each other in efficiency and suitability for specific applications (e.g., solid-phase peptide synthesis or fragment condensation).
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.