440248
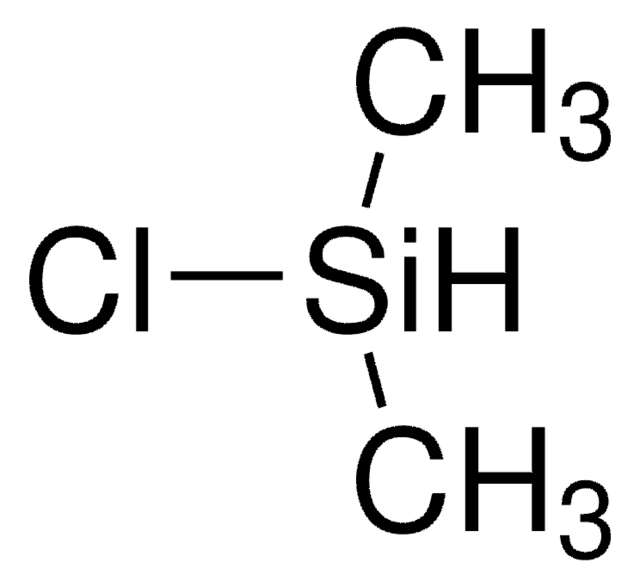
Dichlormethylsilan
≥97%
Synonym(e):
Methyl-dichlorsilan
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Dampfdichte
4 (vs air)
Qualitätsniveau
Dampfdruck
6.79 psi ( 20 °C)
Assay
≥97%
Form
liquid
Selbstzündungstemp.
471 °F
Expl.-Gr.
>55 %
Brechungsindex
n20/D 1.398 (lit.)
bp
41 °C (lit.)
mp (Schmelzpunkt)
−93 °C (lit.)
Dichte
1.105 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
Lagertemp.
2-8°C
SMILES String
C[SiH](Cl)Cl
InChI
1S/CH4Cl2Si/c1-4(2)3/h4H,1H3
InChIKey
NWKBSEBOBPHMKL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Verwandte Kategorien
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
- A General and Selective Synthesis of Methylmonochlorosilanes from Di-, Tri-, and Tetrachlorosilanes - Discusses a method for synthesizing Methylmonochlorosilanes, showing potential for varied applications in chemical synthesis (Y Naganawa et al., 2020).
- Polymerization of methylsilylenes into polymethylsilanes or polycarbosilanes after dechlorination of dichloromethylsilanes. - Investigates the polymerization of methylsilylenes, offering insights into the production of polymethylsilanes or polycarbosilanes from Dichloromethylsilanes (Y Tian et al., 2016).
- Synthesis of low viscosity of polymethylhydrosiloxane using monomer of dichloromethylsilane - Focuses on producing low-viscosity polymethylhydrosiloxane through hydrolysis-condensation of Dichloromethylsilane, significant for various industrial applications (VF Arini et al., 2022).
Verpackung
Signalwort
Danger
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Acute Tox. 3 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Flam. Liq. 2 - Skin Corr. 1A - Water-react 3
Zusätzliche Gefahrenhinweise
Lagerklassenschlüssel
4.3 - Hazardous materials which set free flammable gases upon contact with water
WGK
WGK 1
Flammpunkt (°F)
-18.4 °F
Flammpunkt (°C)
-28 °C
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
Faceshields, Gloves, Goggles
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.