A7469
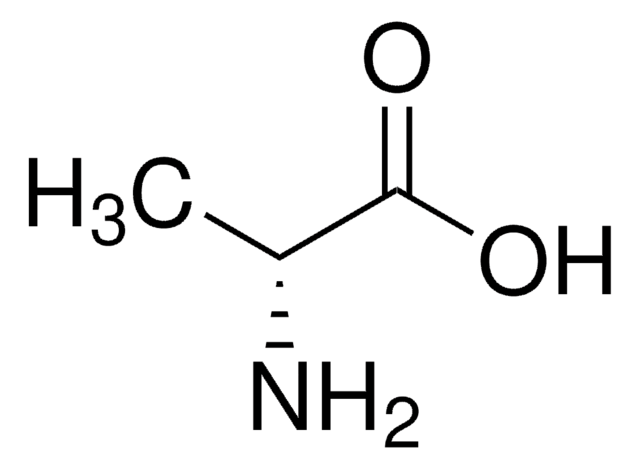
L-Alanine
98.5-101.0%, suitable for cell culture, BioXtra, non-animal source
Sinonimo/i:
(S)-2-Aminopropionic acid, L-α-Aminopropionic acid
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Nome del prodotto
L-Alanine, from non-animal source, meets EP, USP testing specifications, suitable for cell culture, 98.5-101.0%
Origine biologica
non-animal source
Livello qualitativo
agenzia
meets EP testing specifications
meets USP testing specifications
Nome Commerciale
BioXtra
Saggio
98.5-101.0%
Stato
powder
tecniche
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
Impurezze
endotoxin, tested
Colore
white
Solubilità
H2O: 100 mg/mL
applicazioni
peptide synthesis
pharmaceutical (small molecule)
Stringa SMILE
C[C@H](N)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C3H7NO2/c1-2(4)3(5)6/h2H,4H2,1H3,(H,5,6)/t2-/m0/s1
QNAYBMKLOCPYGJ-REOHCLBHSA-N
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Applicazioni
Azioni biochim/fisiol
Applicazioni
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Non trovi la versione di tuo interesse?
Se hai bisogno di una versione specifica, puoi cercare il certificato tramite il numero di lotto.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Muscle
Articoli
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about how proliferatively active cells require both a source of carbon and of nitrogen for the synthesis of macromolecules. Although a large proportion of tumor cells utilize aerobic glycolysis and shunt metabolites away from mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, many tumor cells exhibit increased mitochondrial activity.
Chromatograms
application for HPLCIl team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.