11189
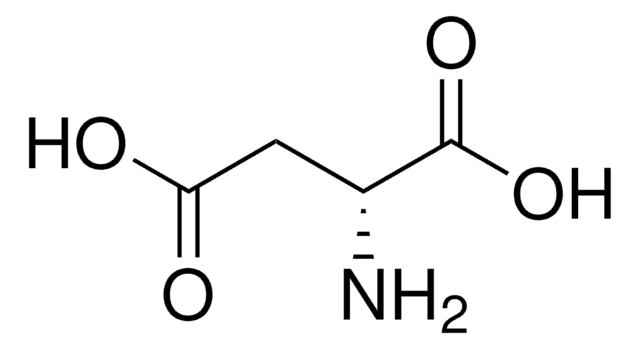
L-Aspartic acid
≥99.5% (T), BioUltra
Sinonimo/i:
(S)-(+)-Aminosuccinic acid, (S)-Aminobutanedioic acid
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
product name
L-Aspartic acid, BioUltra, ≥99.5% (T)
Nome Commerciale
BioUltra
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
≥99.5% (T)
Forma fisica
powder or crystals
Attività ottica
[α]20/D +24.7±1°, c = 5% in 5 M HCl
Impurezze
insoluble matter, passes filter test
≤0.3% foreign amino acids
Residuo alla calcinazione
≤0.05% (as SO4)
Perdita
≤0.1% loss on drying, 110 °C
Colore
white
Punto di fusione
>300 °C (dec.) (lit.)
Solubilità
1 M HCl: 0.5 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless
Anioni in tracce
chloride (Cl-): ≤50 mg/kg
sulfate (SO42-): ≤150 mg/kg
Cationi in tracce
Al: ≤5 mg/kg
As: ≤0.1 mg/kg
Ba: ≤5 mg/kg
Bi: ≤5 mg/kg
Ca: ≤10 mg/kg
Cd: ≤5 mg/kg
Co: ≤5 mg/kg
Cr: ≤5 mg/kg
Cu: ≤5 mg/kg
Fe: ≤5 mg/kg
K: ≤50 mg/kg
Li: ≤5 mg/kg
Mg: ≤5 mg/kg
Mn: ≤5 mg/kg
Mo: ≤5 mg/kg
NH4+: ≤200 mg/kg
Na: ≤100 mg/kg
Ni: ≤5 mg/kg
Pb: ≤5 mg/kg
Sr: ≤5 mg/kg
Zn: ≤5 mg/kg
λ
0.5 M in 1 M HCl
Assorbanza UV
λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.20
λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.10
Stringa SMILE
N[C@@H](CC(O)=O)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C4H7NO4/c5-2(4(8)9)1-3(6)7/h2H,1,5H2,(H,6,7)(H,8,9)/t2-/m0/s1
CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N
Informazioni sul gene
human ... CA1(759) , CA2(760)
rat ... Grin2a(24409)
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
- as a metabolite to study the enzyme–metabolite interactions in the central metabolism of Escherichia coli by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)
- in transmission electron microscopy
- as a component of complete media for culturing Yeast strain
Azioni biochim/fisiol
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.