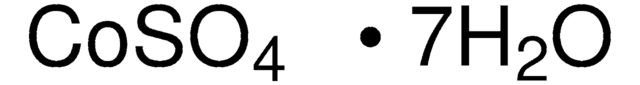C6768
Cobalt(II) sulfate heptahydrate
ReagentPlus®, ≥99%
Sinonimo/i:
Cobaltous sulfate heptahydrate
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Livello qualitativo
Nome Commerciale
ReagentPlus®
Saggio
≥99%
Stato
powder
pH
4 (20 °C, 100 g/L)
Densità
2.03 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
Stringa SMILE
O.[Co++].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O
InChI
1S/Co.H2O4S.H2O/c;1-5(2,3)4;/h;(H2,1,2,3,4);1H2/q+2;;/p-2
BGORGFZEVHFAQU-UHFFFAOYSA-L
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Categorie correlate
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
- Benzazoles from alcohols and o-substituted anilines.
- β-Acetamido ketones via one-pot multi-component coupling reaction of aromatic aldehydes, acetophenones, and acetyl chlorides.
Note legali
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Carc. 1B Inhalation - Eye Irrit. 2 - Muta. 2 - Repr. 1B - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Sens. 1
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
6.1D - Non-combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic hazardous materials or hazardous materials causing chronic effects
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Articoli
Dr. Schmuch, Dr. Siozios, Professor Dr. Winter, and Dr. Placke review the challenges and opportunities of nickelrich layered oxide cathode materials. They discuss production processes for the layered oxide cathode materials as well as their chemistry and morphology.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.