613560
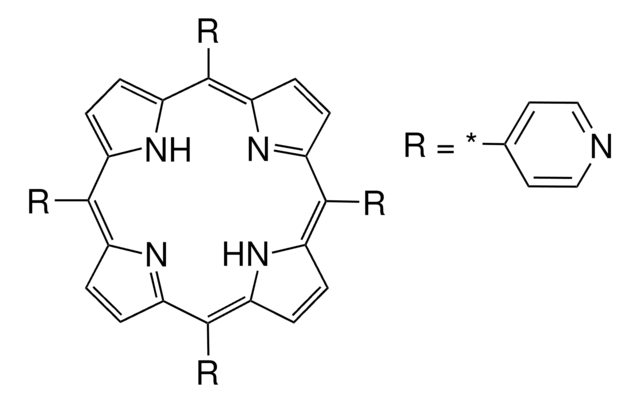
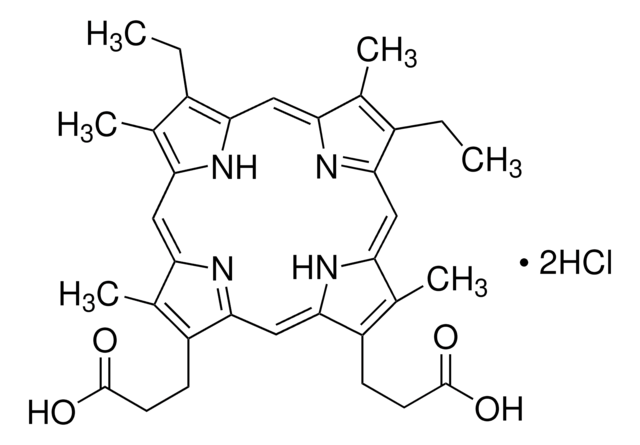
TMPyP4
≥90% (TLC), solid, telomerase inhibitor, Calbiochem®
Sinonimo/i:
TMPyP4, meso-5,10,15,20-Tetrakis-(N-methyl-4-pyridyl)porphine, Tetratosylate
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Nome del prodotto
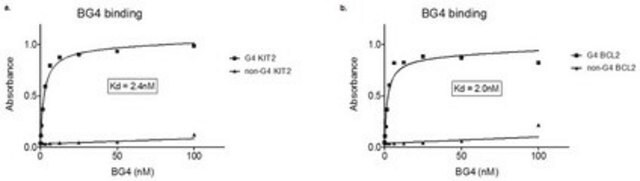
TMPyP4, A potent inhibitor of human telomerase (IC₅₀ = 6.5 µM).
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
≥90% (TLC)
Stato
solid
Produttore/marchio commerciale
Calbiochem®
Condizioni di stoccaggio
OK to freeze
desiccated (hygroscopic)
protect from light
Colore
purple
Solubilità
water: 1 mg/mL
Condizioni di spedizione
ambient
Temperatura di conservazione
2-8°C
InChI
1S/C44H37N8.4C7H8O3S/c1-49-21-13-29(14-22-49)41-33-5-7-35(45-33)42(30-15-23-50(2)24-16-30)37-9-11-39(47-37)44(32-19-27-52(4)28-20-32)40-12-10-38(48-40)43(36-8-6-34(41)46-36)31-17-25-51(3)26-18-31;4*1-6-2-4-7(5-3-6)11(8,9)10/h5-28H,1-4H3,(H,45,46,47,48);4*2-5H,1H3,(H,8,9,10)/q+3;;;;/p-3
AKZFRMNXBLFDNN-UHFFFAOYSA-K
Descrizione generale
Azioni biochim/fisiol
Attenzione
Altre note
Izbicka, E., et al. 1999. Cancer Res. 59, 639.
Anantha, N.V., et al. 1998. Biochemistry 37, 2709.
Arthanari, H., et al. 1998. Nucleic Acids Res. 26, 3724.
Wheelhouse, R.T., et al. 1998. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120, 3261.
Note legali
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.