939374
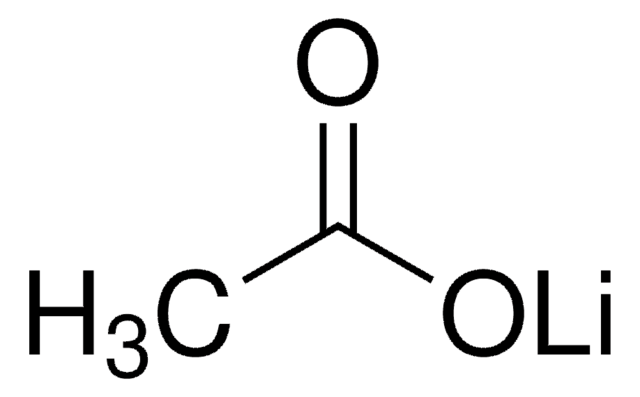
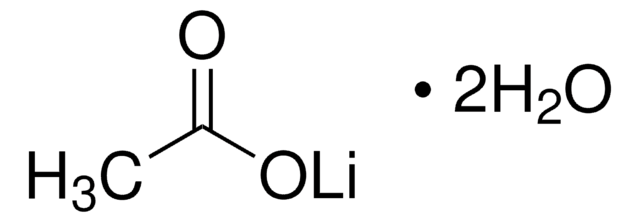
Lithium acetate dihydrate

≥99.9% trace metals basis
Sinonimo/i:
Acetic acid lithium salt, Acetic acid lithium salt dihydrate
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Tipo
(High purity Salts)
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
≥99.9% trace metals basis
Forma fisica
powder or crystals
solid
Impurezze
≤1000 ppm (trace metals analysis)
Colore
white to off-white
pH
≤9.5
Punto di fusione
53-56 °C (lit.)
Solubilità
water: soluble
Anioni in tracce
chloride (Cl-): ≤20 ppm
sulfate (SO42-): ≤50 ppm
Cationi in tracce
Al: <100 ppm
Cu: <100 ppm
Fe: <100 ppm
K: <100 ppm
Mg: <100 ppm
Na: ≤50 ppm
Pb: <100 ppm
Zn: <100 ppm
applicazioni
battery manufacturing
Stringa SMILE
[Li+].[H]O[H].[H]O[H].CC([O-])=O
InChI
1S/C2H4O2.Li.2H2O/c1-2(3)4;;;/h1H3,(H,3,4);;2*1H2/q;+1;;/p-1
IAQLJCYTGRMXMA-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
Our Lithium acetate dihydrate, with a purity of 99.9% on a trace metals basis, serves as an excellent precursor for batteries and catalysis. Its low trace metals content and anions make it particularly well-suited for these applications.
- Lithium Iron Pyrophosphate (LiFe1.5P2O7) with monoclinic structures was successfully synthesized using Lithium acetate dihydrate in combination with other metal acetates, in a ratio of Li/Fe/P = 1.05:1.5:2, through a wet-chemical method. Maintaining the appropriate lithium concentration is crucial to prevent stoichiometry loss in the final product. This material has found application as a positive electrode in Lithium-ion batteries. Remarkably, the electrode demonstrates excellent incremental capacity, indicating a stable structure during the initial cycle, with redox peaks observed at 3.33 and 3.22 V versus Li0/Li+
- LiMn2O4 films were synthesized on Au foil using the sol-gel and spin-coating techniques, employing Lithium acetate dihydrate and manganese acetate tetrahydrate in a Li/Mn ratio of 1.1/2. The particles used had an average size of approximately 300 nm. To investigate the morphological changes during over-discharging, the EC-HS-AFM technique was utilized. The images captured revealed the presence of wrinkle-like and step-like structures on the particle surface. These structures were attributed to stresses induced by structural distortion during the phase transformation from cubic (LiMn2O4) to tetragonal (Li2Mn2O4). The formation of the Li2Mn2O4 phase was confirmed through ex situ XRD analysis. Furthermore, by analyzing the EC-HS-AFM images, the particle surface area was quantitatively extracted as a function of potential, providing insights into the irreversible expansion/contraction behavior of the particles
- Cobalt-free cathodes, specifically Mg and Zr modified LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 (LNMO), were synthesized using Lithium acetate dihydrate and other metal acetates via a citric acid sol-gel method. The modifications aimed to improve the electrochemical performance of the cathode, particularly at high temperatures, by limiting Mn dissolution and adjusting interstitial sites. This modification resulted in increased stability of the cathode, extending the cycle life to 1000 cycles at both 25 and 50 °C
Caratteristiche e vantaggi
- Water soluble
- Medium purity (99.9%)
- Low trace metals in ppm level
- Cost effective
- Low Chloride and sulfate levels
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.