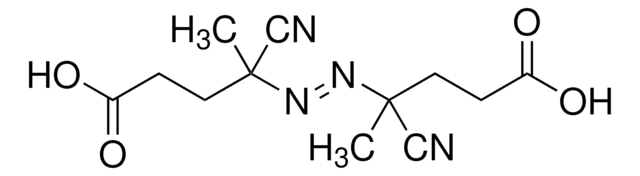
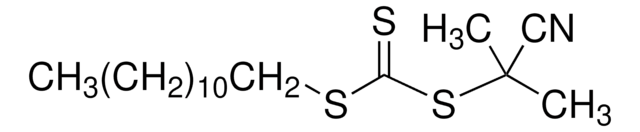
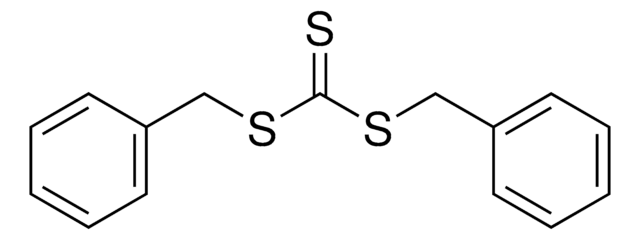
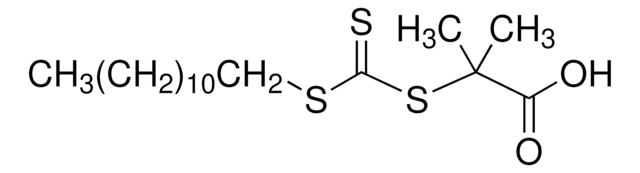
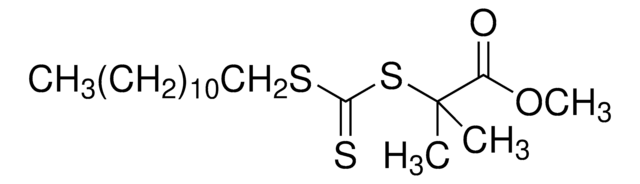
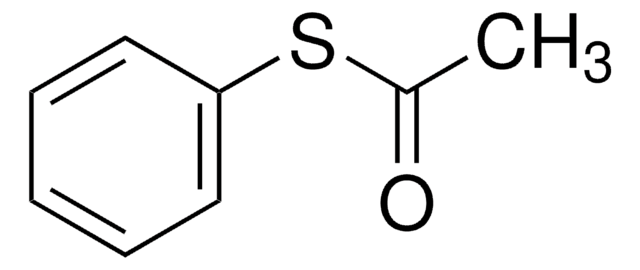
731269
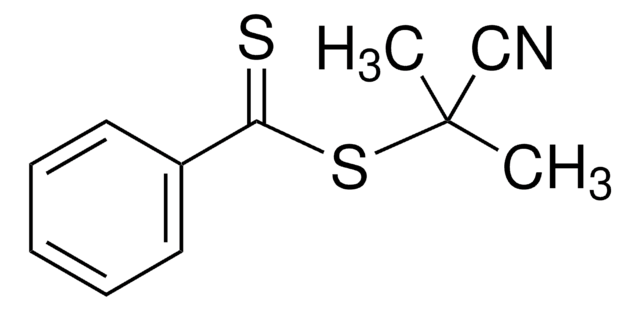
2-Phenyl-2-propyl benzodithioate
99% (HPLC)
Sinonimo/i:
2-Phenylpro-2-yl dithiobenzoate, Benzenecarbodithioic acid 1-methyl-1phenylethyl ester, Cumyl dithiobenzoate
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Saggio
99% (HPLC)
Stato
solid
Densità
1.125 g/mL at 25 °C
Stringa SMILE
CC(C)(SC(=S)c1ccccc1)c2ccccc2
InChI
1S/C16H16S2/c1-16(2,14-11-7-4-8-12-14)18-15(17)13-9-5-3-6-10-13/h3-12H,1-2H3
KOBJYYDWSKDEGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Categorie correlate
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
Avvertenze
Warning
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
219.9 °F
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
104.4 °C
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Articoli
A series of polymerization were carried out using RAFT agents and monomers yielding well-defined polymers with narrow molecular weight distributions.
RAFT (Reversible Addition Fragmentation chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
Over the past two decades, the rapid advance of controlled living polymerization (CLP) techniques.
The modification of biomacromolecules, such as peptides and proteins, through the attachment of synthetic polymers has led to a new family of highly advanced biomaterials with enhanced properties.
Protocolli
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about RAFT, or Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer, which is a form of living radical polymerization.
We presents an article featuring procedures that describe polymerization of methyl methacrylate and vinyl acetate homopolymers and a block copolymer as performed by researchers at CSIRO.
Global Trade Item Number
| SKU | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 731269-5G | 4061832978246 |
| 731269-1G | 4061826280652 |
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.
![4-Cyano-4-[(dodecylsulfanylthiocarbonyl)sulfanyl]pentanoic acid 97% (HPLC)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/204/925/30ae6ca0-5b0b-4963-a061-7e5e3d1a85af/640/30ae6ca0-5b0b-4963-a061-7e5e3d1a85af.png)