L9656
Lipoprotein Lipase from Burkholderia sp.
lyophilized powder, ≥50,000 units/mg solid
Synonyme(s) :
Diacylglycerol acylhydrolase, Diacylglycerol lipase, Lipoprotein Lipase from Pseudomonas sp.
Se connecterpour consulter vos tarifs contractuels et ceux de votre entreprise/organisme
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
Burkholderia spp.
Niveau de qualité
Forme
lyophilized powder
Activité spécifique
≥50,000 units/mg solid
Température de stockage
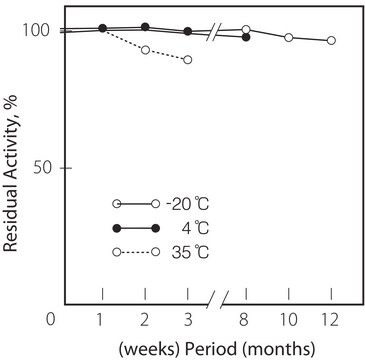
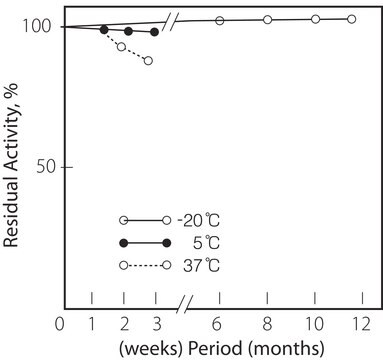
−20°C
Description générale
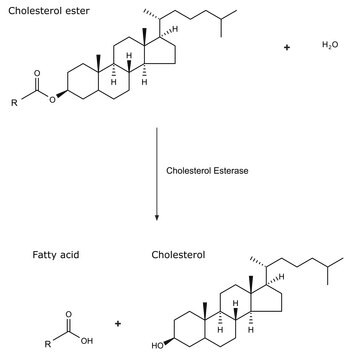
Lipoprotein Lipase (LPL) is a glycerol ester hydrolase. Several bacteria that produce LPL, belongs to the genus Pseudomonas, Serratia and Mucor.
Lipoprotein lipase hydrolyzes triglycerides in plasma lipoproteins causing release of fatty acids for metabolic purposes in muscles and adipose tissue.
Application
Lipoprotein Lipase from Burkholderia sp. has been used in the subcellular fractionation of mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis to identify the biomolecule attached to cytosolic fraction of okodaic acid. It has also been used to test its effect on serum amyloid A induced granulocyte colony-stimulated factor (G-CSF) expression in response to bacterial lipoprotein.LipoproteinLipase from Burkholderia sp. is suitable for the synthesis ofdiarylmethanols, a precursor for the synthesis of pharmaceutical compounds.
Lipoprotein lipase has been used in a study to assess the role of lipogenic enzymes in colorectal cancer. It has also been used in a study to investigate lipasemic activity of low molecular weight heparin in rats.
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Due to its lipolytic activity, lipoprotein lipase was shown to effectively block the spread of hepatitis C virus into healthy cells.
Lipoprotein Lipase (LPL) hydrolysis triacylglycerol moieties in chylomicron and low density lipoproteins. LPL attaches lipoprotein to the vessel wall and facilitates their uptake. Abnormalities in LPL is associated with Alzheimer′s disease, atherosclerosis, obesity and chylomicronaemia.
Lipoprotein lipase belongs to the family of triglyceride lipases. It hydrolyses triglycerides in triglyceride-rich ApoB-containing lipoproteins.
Définition de l'unité
One unit will release 1.0 nmole of p-nitrophenol per min at pH 7.2 at 37 °C using p-nitrophenyl butyrate as substrate.
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Lipoprotein lipase: structure, function, regulation, and role in disease
Mead JR, et al.
Journal of Molecular Medicine, 80(8), 753-769 (2002)
Lipoprotein lipase: from gene to obesity
Wang H and Eckel RH
American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology and Metabolism, 297(8), E271?E288-E271?E288 (2009)
Subcellular distribution of okadaic acid in the digestive gland of Mytilus galloprovincialis: First evidences of lipoprotein binding to okadaic acid
Rossignoli, Araceli E and Blanco, Juan
Toxicon, 55(2-3), 221-226 (2010)
Reiner Thomssen et al.
Medical microbiology and immunology, 191(1), 17-24 (2002-07-26)
In most sera of hepatitis C virus (HCV)-infected patients beta-lipoproteins are bound to HCV RNA-carrying material, most often simultaneously with immunoglobulins (IgG, IgM) and sometimes additionally with high-density lipoproteins, forming complexes of low density (1.04-1.06 g/ml). To separate HCV particles
Studies on the Lipoprotein Lipases of Microorganisms
Arima K, et al.
Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 31(8), 924-929 (1967)
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique