203806
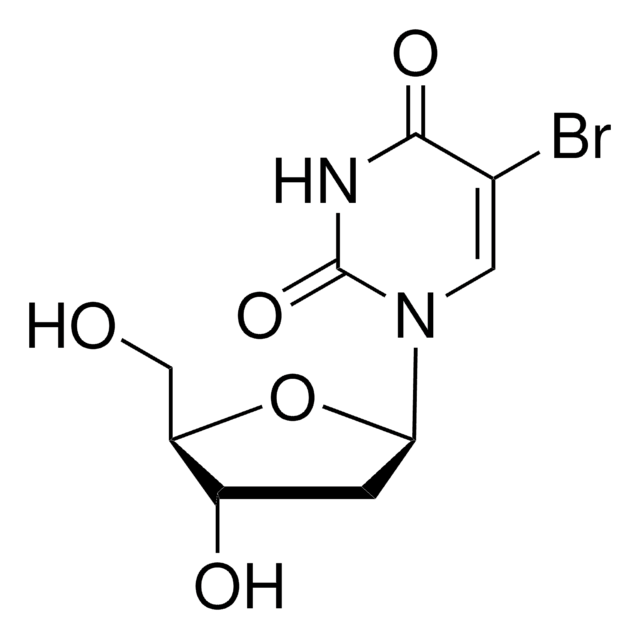
5-Bromo-2′-deoxyuridine
Thymidine analog. Useful for the study of DNA synthesis where it is incorporated into DNA in place of thymidine.
Synonyme(s) :
5-Bromo-2′-deoxyuridine, 5-BrdU
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Essai
≥98% (HPLC)
Forme
solid
Fabricant/nom de marque
Calbiochem®
Conditions de stockage
OK to freeze
Couleur
white
Solubilité
water: 10 mg/mL
0.1 M NaOH: 50 mg/mL
DMSO: 50 mg/mL
Conditions d'expédition
ambient
Température de stockage
15-25°C
Chaîne SMILES
Brc1[c]([nH][c]([n](c1)C2OC(C(C2)O)CO)=O)=O
InChI
1S/C9H11BrN2O5/c10-4-2-12(9(16)11-8(4)15)7-1-5(14)6(3-13)17-7/h2,5-7,13-14H,1,3H2,(H,11,15,16)
Clé InChI
WOVKYSAHUYNSMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Description générale
Avertissement
Reconstitution
Autres remarques
Cattoretti, G., et al. 1993. J. Pathol. 171, 83.
Fukuda, K., et al. 1990. Anal. Quant. Cytol. Histol. 12, 135.
Informations légales
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Muta. 1B - Repr. 2
Code de la classe de stockage
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 2
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique