C1930
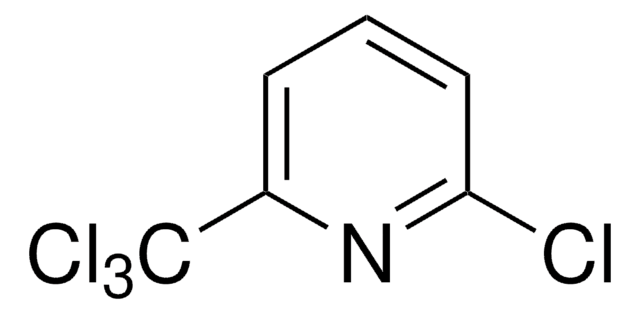
2-Chloro-6-(trichloromethyl)pyridine
≥98%
Synonyme(s) :
Nitrapyrin
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Agence
suitable for SM 5210
Niveau de qualité
Essai
≥98%
Forme
powder
Solubilité
ethanol: 10 mg/mL, clear, colorless to faintly yellow
Chaîne SMILES
Clc1cccc(n1)C(Cl)(Cl)Cl
InChI
1S/C6H3Cl4N/c7-5-3-1-2-4(11-5)6(8,9)10/h1-3H
Clé InChI
DCUJJWWUNKIJPH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Application
- Biological and chemical nitrification inhibitors exhibited different effects on soil gross N nitrification rate and N(2)O production: a (15)N microcosm study.: This study examines the effects of biological and chemical nitrification inhibitors, including 2-Chloro-6-(trichloromethyl)pyridine, on soil nitrogen processes. The findings highlight the differential impacts on soil nitrogen dynamics and greenhouse gas emissions (Lan et al., 2023).
- Nitrous oxide emissions from manured soils as a function of various nitrification inhibitor rates and soil moisture contents.: This paper explores the relationship between nitrification inhibitor application rates, including 2-Chloro-6-(trichloromethyl)pyridine, and soil moisture on nitrous oxide emissions, providing insights into optimizing inhibitor use for environmental benefits (Lin and Hernandez-Ramirez, 2020).
- Nitrate losses in subsurface drainage from a corn-soybean rotation as affected by fall and spring application of nitrogen and nitrapyrin.: Investigating the seasonal application of nitrapyrin, a derivative of 2-Chloro-6-(trichloromethyl)pyridine, this study assesses its efficacy in reducing nitrate leaching and improving nitrogen use efficiency in agricultural systems (Randall and Vetsch, 2005).
- Oxidation of Nitrapyrin to 6-Chloropicolinic Acid by the Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacterium Nitrosomonas europaea.: This foundational research elucidates the microbial degradation pathway of nitrapyrin, contributing to our understanding of its environmental fate and persistence (Vannelli and Hooper, 1992).
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 2
Code de la classe de stockage
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 2
Point d'éclair (°F)
212.0 °F - closed cup
Point d'éclair (°C)
100 °C - closed cup
Équipement de protection individuelle
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique