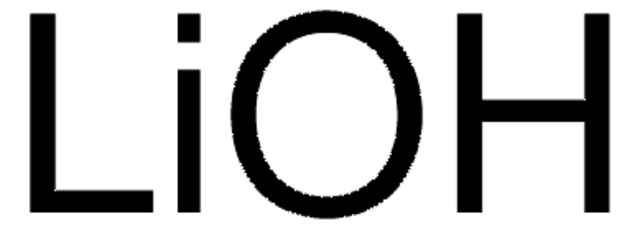
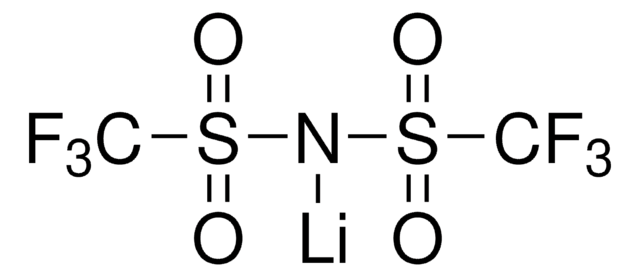
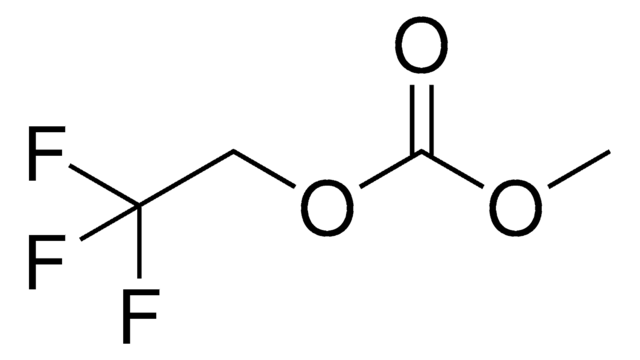
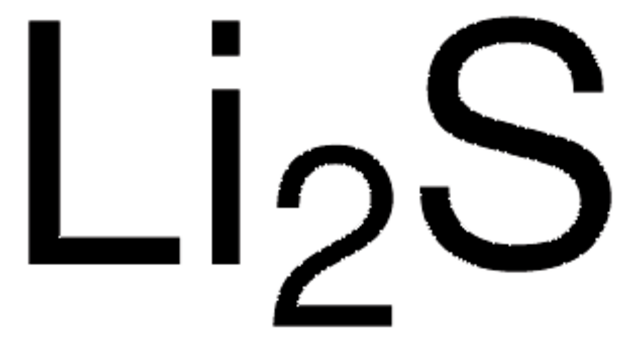930946
Lithium nitrate
battery grade, ≥99.9% trace metals basis
Synonyme(s) :
Lithium salt of nitric acid
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Qualité
battery grade
Essai
≥99.9% trace metals basis
Forme
powder
Caractéristiques du produit alternatif plus écologique
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
Impuretés
≤0.5 wt. % H2O
≤1000 ppm (trace metals analysis)
Pf
264 °C (lit.)
Solubilité
H2O: soluble (highly soluble(lit.))
acetone: soluble ((lit.))
alcohols: soluble ((lit.))
Traces d'anions
chloride (Cl-): ≤500 ppm
sulfate (SO42-): ≤200 ppm
Application(s)
battery manufacturing
Autre catégorie plus écologique
Chaîne SMILES
[Li+].[O-][N+]([O-])=O
InChI
1S/Li.NO3/c;2-1(3)4/q+1;-1
Clé InChI
IIPYXGDZVMZOAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Catégories apparentées
Description générale
Lithium nitrate is produced by the acid-base reaction between nitric acid and lithium carbonate, which evolves carbon dioxide and water. The resulting material is dried, purified, and heated to form the anhydrous product.
Application
Because lithium nitrate is soluble in water, researchers also use lithium nitrate in the synthesis of lithium compounds using a host of solution-based chemistries. For example, microwave-induced combustion using solutions of lithium nitrate has yielded olivine-type lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2), and lithium titanium oxides (ex. Li4Ti5O12 and Li2TiO3). Hydrothermal processing, sol-gel processing, spray pyrolysis, co-precipitation pre-processing, and Li emulsion-drying methods have all used lithium nitrate as a reactant to form lithium metal oxides. These techniques can yield controlled particle size, grain size, crystallinity, or facilitate the introduction of dopants for engineering the properties of the products, often explored for next-generation lithium-ion batteries.
Our battery grade lithium nitrate with ≥99.9% trace metals purity and low chloride and sulfate impurities, is designed as a precursor for cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries.
Mention d'avertissement
Warning
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Irrit. 2 - Ox. Sol. 3
Code de la classe de stockage
5.1B - Oxidizing hazardous materials
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 1
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documents section.
Si vous avez besoin d'assistance, veuillez contacter Service Clients
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique