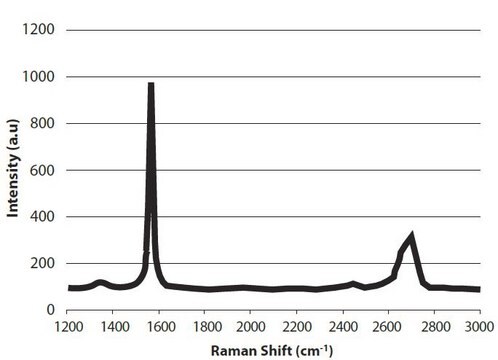
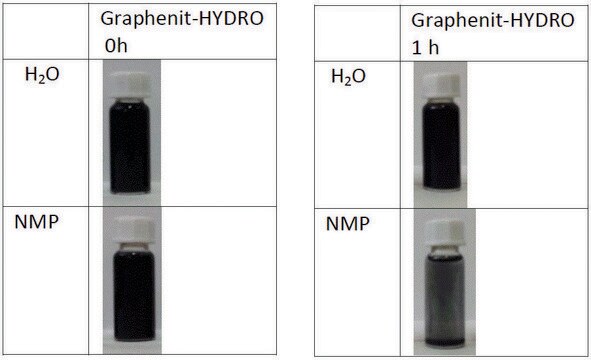
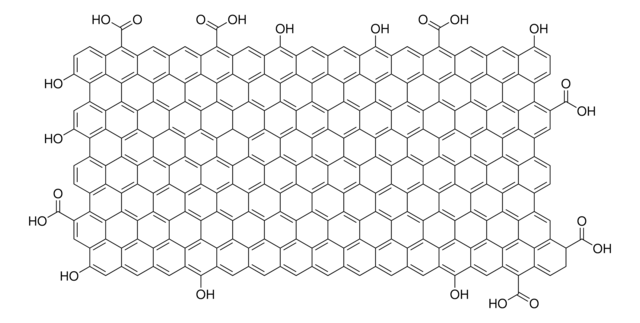
806668
Graphene nanoplatelets
powder, hydrophobic
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Forme
powder
Composition
Carbon, >95 wt. %
Oxygen, <2 wt. %
Masse volumique apparente
0.04 g/mL
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Application
- Graphene (nano)composite materials
- Conductive coatings
- Anti-corrosion coatings
- Conductive Inks
- Energy Storage
- Electrode materials
Mention d'avertissement
Warning
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Eye Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Organes cibles
Respiratory system
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Vous ne trouvez pas la bonne version ?
Si vous avez besoin d'une version particulière, vous pouvez rechercher un certificat spécifique par le numéro de lot.
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
Advanced technologies for energy conversion and storage are widely sought after for their potential to improve consumer and electronic device performance as well as for the prospect of reducing the societal and environmental impact of energy generation.
Since its discovery little more than a decade ago,1 the two-dimensional (2D) allotrope of carbon—graphene—has been the subject of intense multidisciplinary research efforts.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique