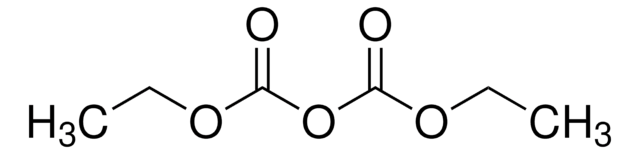
40718
Pyrocarbonate de diéthyle
96% (NT)
Synonyme(s) :
Anhydride éthoxyformique, DEP, DEPC, Dicarbonate de diéthyle, Oxydiformiate de diéthyle
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Essai
96% (NT)
Forme
liquid
Couleur
APHA: ≤20
Indice de réfraction
n20/D 1.398 (lit.)
n20/D 1.398
pb
93-94 °C/18 mmHg (lit.)
Solubilité
95% ethanol: 4.5 g/10 mL, clear, colorless
Densité
1.121 g/mL at 20 °C
1.101 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
Groupe fonctionnel
carbonate
Conditions d'expédition
wet ice
Température de stockage
2-8°C
Chaîne SMILES
CCOC(=O)OC(=O)OCC
InChI
1S/C6H10O5/c1-3-9-5(7)11-6(8)10-4-2/h3-4H2,1-2H3
Clé InChI
FFYPMLJYZAEMQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Catégories apparentées
Description générale
Application
- For the modification of histidyl residues in proteins.
- As a nuclease inhibitor, for the extraction of undegraded nucleic acids from etiolated and green plant tissues.
- For the modification of linear and supercoiled plasmid DNAs.
- As a chemical probe to investigate the secondary structure in negatively supercoiled DNA.
- For cabethoxylation of histidine residues of actin.
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Mention d'avertissement
Warning
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Acute Tox. 4 Oral
Code de la classe de stockage
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
156.2 °F - closed cup
Point d'éclair (°C)
69 °C - closed cup
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique