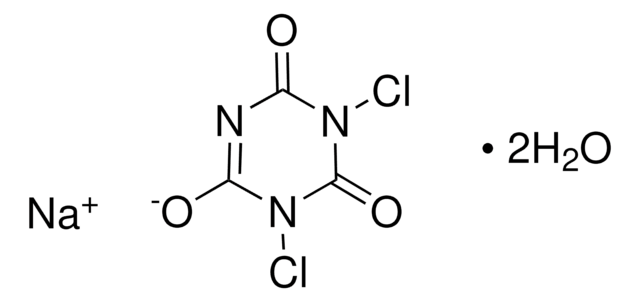
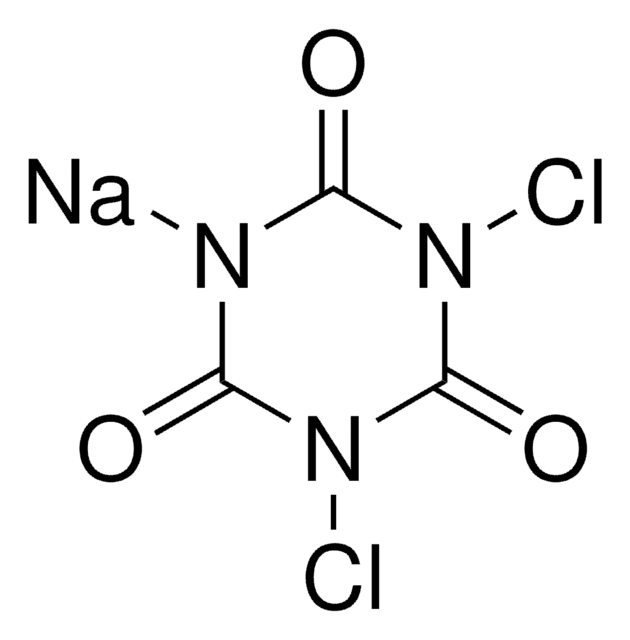
379867
Potassium dicyanoaurate(I)
99.95% trace metals basis
Synonyme(s) :
Gold (I) potassium cyanide, Potassium gold cyanide
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Pureté
99.95% trace metals basis
Forme
crystalline
Impuretés
≤550.0 ppm Trace Metal Analysis
Densité
3.45 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
Chaîne SMILES
[K+].N#C[Au-]C#N
InChI
1S/2CN.Au.K/c2*1-2;;/q;;-1;+1
Clé InChI
OQHPFUBKFKRHKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Application
- To prepare gold nanowire array electrodes with fast charge transfer ability.
- As a supporting electrolyte for the electrodeposition of gold in organic media.
- To prepare polypyrrole-ClO4 gas sensors with fast response time and high sensitivity to volatile organic compounds.
- In the electrochemical preparation of gold nanoparticle composites.
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Acute Tox. 1 Dermal - Acute Tox. 2 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 2 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1
Risques supp
Code de la classe de stockage
6.1B - Non-combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique
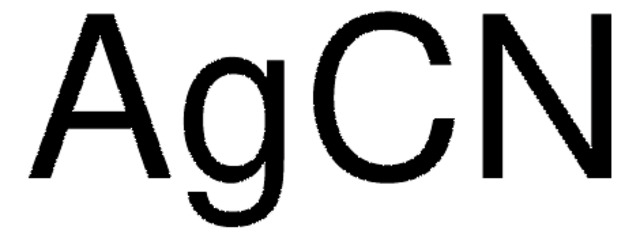
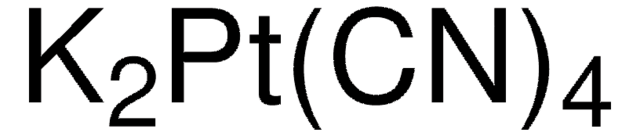

![Cyanide standard solution traceable to SRM from NIST K₂[Zn(CN)₄] in H₂O 1000 mg/l CN Certipur®](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/images/920/032/af45eec3-100b-4996-8eb3-c3942d441bc9/640/af45eec3-100b-4996-8eb3-c3942d441bc9.jpg)