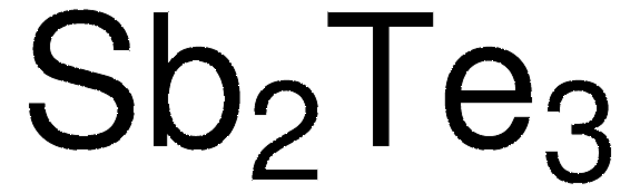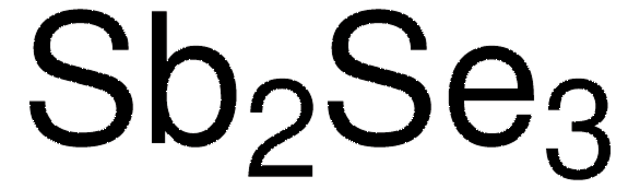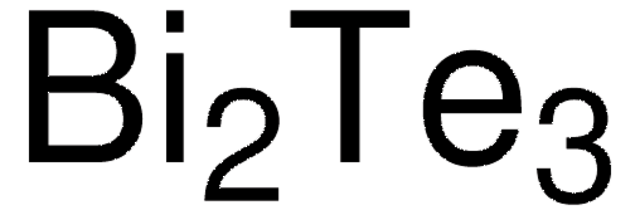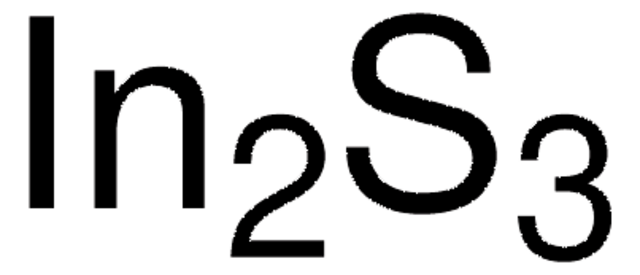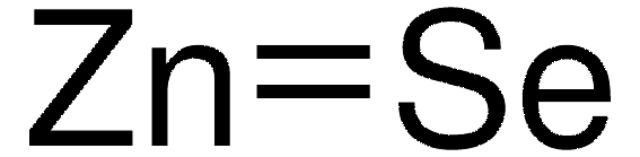254266
Lead(II) telluride
99.998% trace metals basis
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Pureté
99.998% trace metals basis
Forme
crystals and lumps
Caractéristiques du produit alternatif plus écologique
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
Pf
905 °C (lit.)
Densité
8.164 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
Autre catégorie plus écologique
, Enabling
Chaîne SMILES
[Te]=[PbH2]
InChI
1S/Pb.Te
Clé InChI
OCGWQDWYSQAFTO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Description générale
Application
Conditionnement
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Carc. 2 - Repr. 1A - STOT RE 2
Code de la classe de stockage
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
Thermoelectric materials comprise a wide range of solid compounds distinguished by their ability to convert thermal and electrical energy.
In recent years, the price of tellurium, a key component in the bestperforming thermoelectric materials, has increased significantly, leading to the question, “Is it economically viable to produce thermoelectric generators on an industrial scale?
The price of tellurium, a key component in many thermoelectric materials, has risen in recent years, leading to the search for more cost-effective substitutes. This article presents silicide materials as a cheaper potential alternative.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique