C3556
Catalase from human erythrocytes
≥90% (SDS-PAGE), buffered aqueous solution, ≥30,000 units/mg protein
Synonym(s):
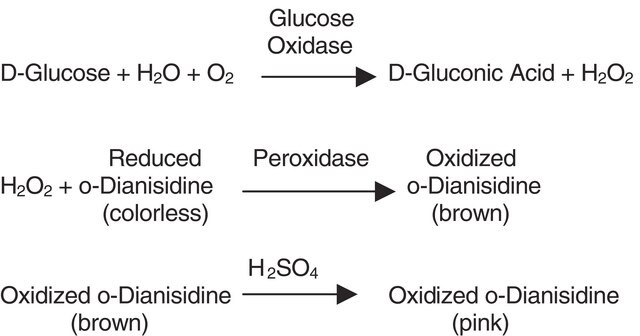
H2O2:H2O2 oxidoreductase
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
human erythrocytes
Quality Level
Assay
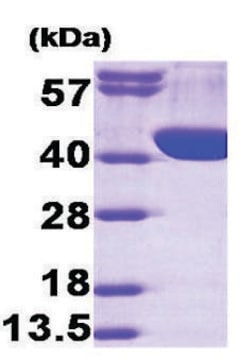
≥90% (SDS-PAGE)
form
buffered aqueous solution
specific activity
≥30,000 units/mg protein
mol wt
tetramer ~250 kDa
concentration
≤10 mg/mL
technique(s)
cell based assay: suitable
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
InChI
1S/C9H10O3/c1-2-12-9(11)7-3-5-8(10)6-4-7/h3-6,10H,2H2,1H3
InChI key
NUVBSKCKDOMJSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Gene Information
human ... CAT(847)
General description
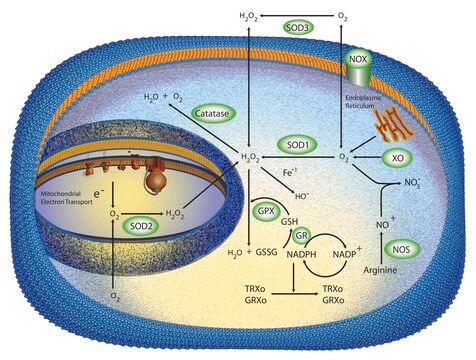
Human catalase is a member of the monofunctional heme-containing catalases. It is an intracellular enzyme located at higher concentrations in the liver, erythrocytes, and kidney. Catalase is a homo-tetrameric protein and comprises amino acid residues, one heme group that is iron III protoporphyrin IX, and a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) molecule. It is a ubiquitous enzyme found in most aerobic organisms. The catalase (CAT) gene is located on the human chromosome at 11p13.
Application
- to prevent reoxidation of reduced cytochrome c by H2O2 while measuring the production of superoxide with cytochrome C.
- as a component of the imaging buffer for stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM) imaging of human skin fibroblasts
- as a component of the gloxy mix for single-molecule imaging
Biochem/physiol Actions
Unit Definition
Physical form
Storage and Stability
persons
Analysis Note
inhibitor
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Oxidative stress is mediated, in part, by reactive oxygen species produced by multiple cellular processes and controlled by cellular antioxidant mechanisms such as enzymatic scavengers or antioxidant modulators. Free radicals, such as reactive oxygen species, cause cellular damage via cellular.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service