SCP0076
Caspase 2 Inhibitor (ICH-1)
Anmeldenzur Ansicht organisationsspezifischer und vertraglich vereinbarter Preise
Alle Fotos(1)
About This Item
Empirische Formel (Hill-System):
C23H37N5O10
Molekulargewicht:
543.57
UNSPSC-Code:
12352200
NACRES:
NA.32
Empfohlene Produkte
Assay
≥95% (HPLC)
Form
lyophilized
Zusammensetzung
Peptide Content, ≥80%
Lagerbedingungen
protect from light
Lagertemp.
−20°C
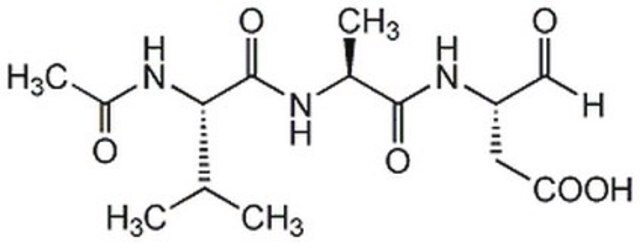
Amino Acid Sequence
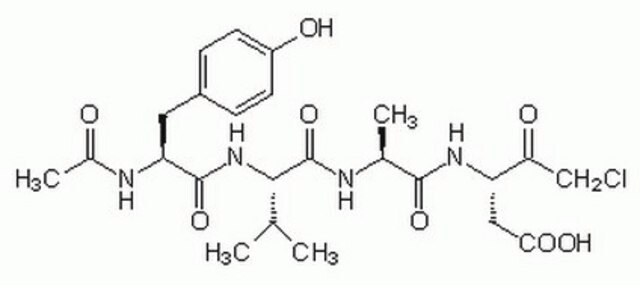
Ac-Val-Asp-Val-Ala-Asp-al
Anwendung
Caspase 2 Inhibitor (Ac-VDVAD-CHO) is a non-selective (also inhibits caspase 3) but powerful inhibitor of caspase 2 used to study the role of caspase 2 in cell processes.
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Die passende Version wird nicht angezeigt?
Wenn Sie eine bestimmte Version benötigen, können Sie anhand der Lot- oder Chargennummer nach einem spezifischen Zertifikat suchen.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Michel C Maillard et al.
Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry, 19(19), 5833-5851 (2011-09-10)
Several caspases have been implicated in the pathogenesis of Huntington's disease (HD); however, existing caspase inhibitors lack the selectivity required to investigate the specific involvement of individual caspases in the neuronal cell death associated with HD. In order to explore
Bin Fang et al.
Journal of molecular biology, 360(3), 654-666 (2006-06-20)
The molecular basis for the substrate specificity of human caspase-3 has been investigated using peptide analog inhibitors and substrates that vary at the P2, P3, and P5 positions. Crystal structures were determined of caspase-3 complexes with the substrate analogs at
Ju Youn Kim et al.
Cell, 175(1), 133-145 (2018-09-18)
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) progresses to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in response to elevated endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Whereas the onset of simple steatosis requires elevated de novo lipogenesis, progression to NASH is triggered by accumulation of hepatocyte-free cholesterol. We
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.