R1753
Ribonukleinsäure, Transfer aus E. coli
Type XX, Strain W, lyophilized powder
Synonym(e):
Transfer-RNA, tRNA
Anmeldenzur Ansicht organisationsspezifischer und vertraglich vereinbarter Preise
Alle Fotos(3)
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Anwendung
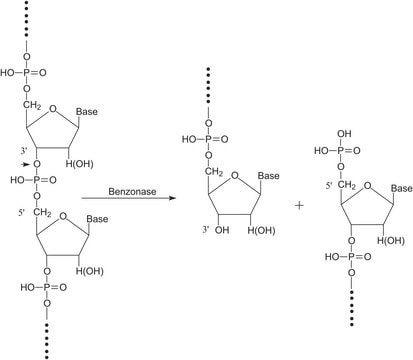
Von Escherichia coli, Typ XX, Stamm W transferierte Ribonukleinsäure kann als Ausgangsmaterial für die Aufreinigung bestimmter Aminoacyl-tRNA-Spezies durch Verfahren wie Flüssigsäulen- oder Hochleistungsflüssigkeitschromatographie (HPLC) verwendet werden.
Einheitendefinition
Eine Einheit liefert ein A260 von 1,0 in 1,0 ml Wasser (1-cm-Lichtweg).
Hinweis zur Analyse
Jede Charge wird mit Aminoacyl-tRNA-Synthetase und einer Mischung der Aminosäuren Ala, Asp, Gly, Ile, Lys, Pro, Thr, Val, Arg, Glu, His, Leu, Phe, Ser und Tyr auf ihre Aminosäurenakzeptoraktivität geprüft.
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Roya Pedram Fatemi et al.
Journal of biomolecular screening, 20(9), 1132-1141 (2015-07-16)
Long non-protein coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are an important class of molecules that help orchestrate key cellular events. Although their functional roles in cells are not well understood, thousands of lncRNAs and a number of possible mechanisms by which they act
Fuxiang Wei et al.
Nature communications, 11(1), 4902-4902 (2020-10-01)
Living cells and tissues experience various complex modes of forces that are important in physiology and disease. However, how different force modes impact gene expression is elusive. Here we apply local forces of different modes via a magnetic bead bound
Thomas E Sladewski et al.
eLife, 7 (2018-06-27)
We investigated the role of full-length Drosophila Bicaudal D (BicD) binding partners in dynein-dynactin activation for mRNA transport on microtubules. Full-length BicD robustly activated dynein-dynactin motility only when both the mRNA binding protein Egalitarian (Egl) and K10 mRNA cargo were
Adi Egozi et al.
Cell reports, 32(7), 108043-108043 (2020-08-20)
The islets of Langerhans are dynamic structures that can change in size, number of cells, and molecular function in response to physiological and pathological stress. Molecular cues originating from the surrounding "peri-islet" acinar cells that could facilitate this plasticity have
Jean Lehmann et al.
Nucleic acids research, 41(10), 5494-5502 (2013-04-13)
The structure and function of conserved motifs constituting the apex of Stem I in T-box mRNA leaders are investigated. We point out that this apex shares striking similarities with the L1 stalk (helices 76-78) of the ribosome. A sequence and
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.