Alle Fotos(1)
Wichtige Dokumente
P3895
Phosphatase alkalisch aus menschlicher Placenta
≥10 units/mg solid (in glycine buffer)
Synonym(e):
Orthophosphoric-monoester phosphohydrolase (alkaline optimum)
Anmeldenzur Ansicht organisationsspezifischer und vertraglich vereinbarter Preise
Alle Fotos(1)
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Form
solid
Qualitätsniveau
Spezifische Aktivität
≥10 units/mg solid (in glycine buffer)
UniProt-Hinterlegungsnummer
Lagertemp.
−20°C
Angaben zum Gen
human ... ALPP(250)
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Anwendung
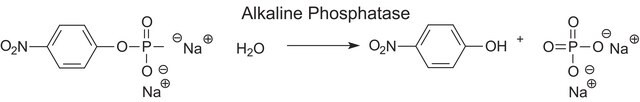
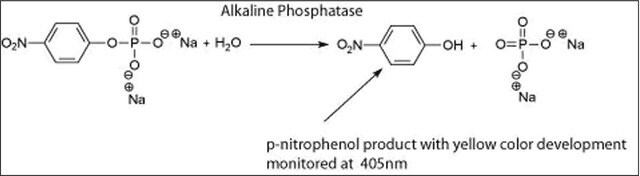
Alkaline phosphatase is used for conjugation to antibodies and other proteins for ELISA, Western blotting, and histochemical detection. It is routinely used to dephosphorylate proteins and nucleic acids. It may be used for protein labeling when high sensitivity is required. Alkaline phosphatase may be also be used to dephosphorylate the 5′-termini of DNA or RNA to prevent self-ligation. DNA or RNA can also be tagged with radiolabeled phosphate (via T4 polynucleotide kinase) after dephosphorylation with alkaline phosphatase.
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
Alkaline phosphatase dephosphorylates proteins and nucleic acids. Human placental alkaline phosphatase (PLAP) has an unique residue, Glu-429. It is an allosteric enzyme that is uncompetitively inhibited by L-Phe, L-Trp, and L-Leu. PLAP is post-translationally modified. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C may be involved in the release of PLAP. PLAP may have a role in cell division and may be involved in the transfer of maternal IgG to the fetus.
Einheitendefinition
One unit will hydrolyze 1 μmole of 4-nitrophenyl phosphate per minute at pH 10.4 at 37 °C.
Inhibitor
Produkt-Nr.
Beschreibung
Preisangaben
Signalwort
Danger
H-Sätze
P-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Resp. Sens. 1
Lagerklassenschlüssel
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
M H Le Du et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 276(12), 9158-9165 (2001-01-01)
Human placental alkaline phosphatase (PLAP) is one of three tissue-specific human APs extensively studied because of its ectopic expression in tumors. The crystal structure, determined at 1.8-A resolution, reveals that during evolution, only the overall features of the enzyme have
Ashleigh M Philp et al.
Scientific reports, 7(1), 4042-4042 (2017-06-24)
The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of adiposity on the architecture and composition of hip OA subchondral bone, and to examine the pathological role of adipokines. Femoral heads were collected from normal-weight or over-weight/obese patients with
Jong Kil Lee et al.
The Journal of experimental medicine, 211(8), 1551-1570 (2014-07-23)
In Alzheimer's disease (AD), abnormal sphingolipid metabolism has been reported, although the pathogenic consequences of these changes have not been fully characterized. We show that acid sphingomyelinase (ASM) is increased in fibroblasts, brain, and/or plasma from patients with AD and
A D Bakker et al.
Journal of dental research, 93(4), 394-399 (2014-02-05)
Mechanosensitive osteocytes regulate bone mass in adults. Interleukin 6 (IL-6), such as present during orthodontic tooth movement, also strongly affects bone mass, but little is known about the effect of IL-6 on osteocyte function. Therefore we aimed to determine in
M D McKee et al.
Journal of dental research, 92(8), 721-727 (2013-05-23)
Phosphatases are involved in bone and tooth mineralization, but their mechanisms of action are not completely understood. Tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNAP, ALPL) regulates inhibitory extracellular pyrophosphate through its pyrophosphatase activity to control mineral propagation in the matrix; mice without TNAP
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.