A4268
α-Amylase aus Schweinepankreas
Type I-A, PMSF treated, saline suspension, 700-1400 units/mg protein (E1%/280)
Synonym(e):
β-N-Acetylglucosaminidase, Schweineplazenta, PPA, Schweinepankreas α-Amylase, al1,4-Glucan-4-glucanohydrolase,
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Biologische Quelle
Porcine pancreas
Qualitätsniveau
Typ
Type I-A
Form
saline suspension
Spezifische Aktivität
700-1400 units/mg protein (E1%/280)
Mol-Gew.
51-54 kDa
Grünere Alternativprodukt-Eigenschaften
Waste Prevention
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
Methode(n)
activity assay: suitable
Eignung
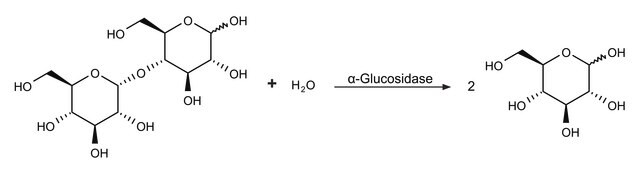
suitable for hydrolysis, synthesis of oligosaccharides and polysaccharides, and sugar modification
Anwendung(en)
diagnostic assay manufacturing
Grünere Alternativprodukt-Kategorie
, Enabling
Lagertemp.
2-8°C
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Allgemeine Beschreibung
α-Amylase, isoliert aus Schweine-Pankreas, ist ein Glykoprotein. Sie ist eine einzelne Polypeptidkette von ~475 Resten, die zwei SH-Gruppen und vier Disulfidbrücken sowie dicht gebundenes Ca2+ für die Stabilität enthält. Chloridionen sind notwendig für Aktivität und Stabilität. Der pH-Wertbereich für Aktivität beträgt 5,5 bis 8,0, wobei der optimale pH-Wert bei 7 liegt.
Anwendung
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
Einheitendefinition
Physikalische Form
Angaben zur Herstellung
Sonstige Hinweise
Inhibitor
Substrat
Signalwort
Danger
H-Sätze
P-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Resp. Sens. 1
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.