Wichtige Dokumente
STS0214
Brij® 98
average Mn ~1,150
Synonym(e):
Polyoxyethylen (20)oleylether
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Beschreibung
non-ionic
Qualitätsniveau
Form
solid
Mol-Gew.
average Mn ~1,150
Grünere Alternativprodukt-Eigenschaften
Use of Renewable Feedstocks
Design for Degradation
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
mp (Schmelzpunkt)
25-30 °C (lit.)
Hydroxylzahl
50‑65 mg KOH/g
Löslichkeit
water: soluble 1 g/L at 20 °C
Dichte
0.901 g/cm3 at 20 °C
HLB
15.5
Grünere Alternativprodukt-Kategorie
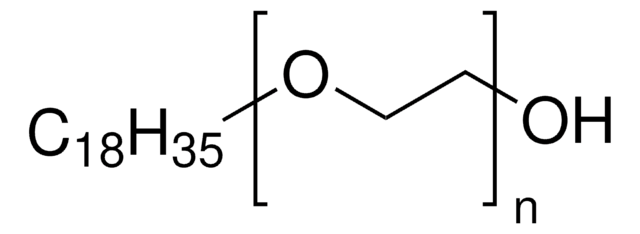
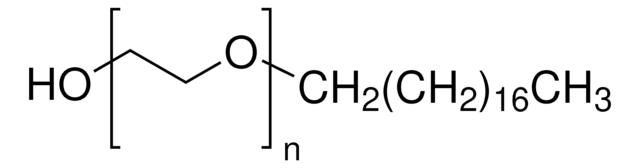
SMILES String
O(CCO)CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC
InChI
1S/C20H40O2/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-19-22-20-18-21/h9-10,21H,2-8,11-20H2,1H3/b10-9-
InChIKey
KWVPFECTOKLOBL-KTKRTIGZSA-N
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Leistungsmerkmale und Vorteile
- 100 % Renewable
- 100 % Bio-based
- Certified to the USDA BioPreferred Program
- Lower carbon footprint than petrochemical-based versions
- High-purity chemical suitable for a wide variety of research applications
Sonstige Hinweise
Rechtliche Hinweise
Signalwort
Warning
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Aquatic Chronic 2 - Skin Irrit. 2
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flammpunkt (°F)
>464.0 °F - Equilibrium method
Flammpunkt (°C)
> 240 °C - Equilibrium method
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Dokumente section.
Wenn Sie Hilfe benötigen, wenden Sie sich bitte an Kundensupport
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.