5291
Polymyxin-B-Sulfat
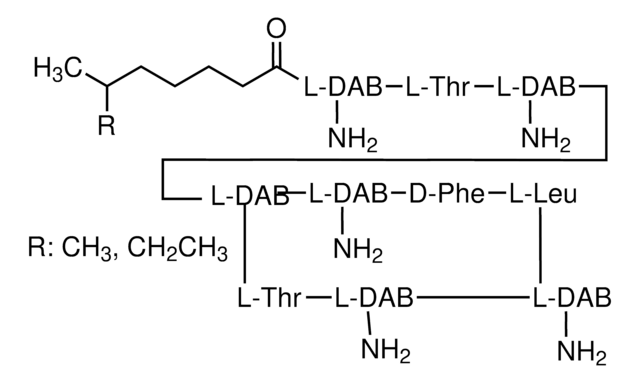
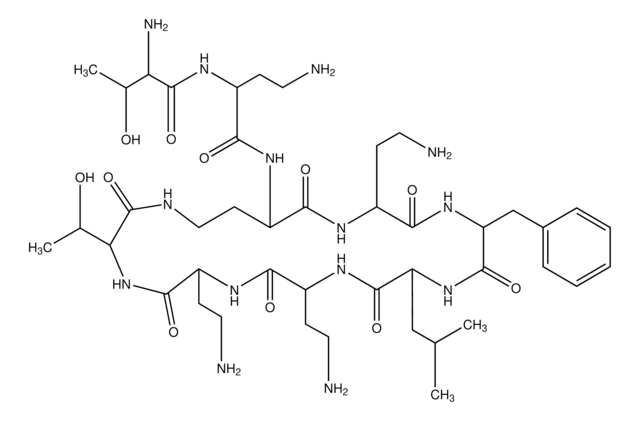
Polymyxin B Sulfate, CAS 1405-20-5, is an antibiotic that is effective against Gram-positive bacteria. Inhibits phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinases.
Synonym(e):
Polymyxin-B-Sulfat
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualitätsniveau
Form
solid
Hersteller/Markenname
Calbiochem®
Lagerbedingungen
OK to freeze
Farbe
white to off-white
Löslichkeit
water: 25 mg/mL
Versandbedingung
ambient
Lagertemp.
10-30°C
InChI
1S/C48H82N16O13.H2O4S/c1-27(2)24-37-47(76)59-32(11-19-52)41(70)56-31(10-18-51)43(72)61-35(14-22-65)39(68)54-21-13-34(45(74)57-33(12-20-53)44(73)64-38(48(77)63-37)25-28-6-4-3-5-7-28)60-42(71)30(9-17-50)58-46(75)36(15-23-66)62-40(69)29(8-16-49)55-26-67;1-5(2,3)4/h3-7,26-27,29-38,65-66H,8-25,49-53H2,1-2H3,(H,54,68)(H,55,67)(H,56,70)(H,57,74)(H,58,75)(H,59,76)(H,60,71)(H,61,72)(H,62,69)(H,63,77)(H,64,73);(H2,1,2,3,4)
InChIKey
HNDFYNOVSOOGDU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
- zum Neutralisieren der Endotoxine in Rinderserumsalbumin
- bei der In-vitro-Behandlung von Kupffer-Sternzellen
- als Antibiotikum bei der Analyse der kollateralen Sensitivität und Kreuzresistenz in Escherichia coli
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
Warnhinweis
Sonstige Hinweise
Ngezahayo, A. and Kolb, H.A. 1993. Pflugers Arch.422, 413.
Kubo, M. und Okada, Y. 1992. J. Physiol.456, 351.
Strasser, S.H., et al. 1992. Circ. Res.70, 1304.
Hegemann, L., et al. 1991. Eur. J. Pharmacol.207, 17.
Inaba, H. und Filkins, J.P. 1991. Am. J. Physiol.261, R26.
Marra, M.N., et al. 1990. J. Immunol.144, 662.
Rechtliche Hinweise
Signalwort
Warning
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Acute Tox. 4 Oral
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.