810600P
Avanti
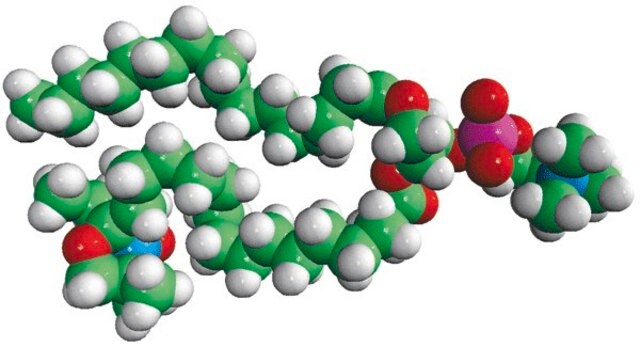
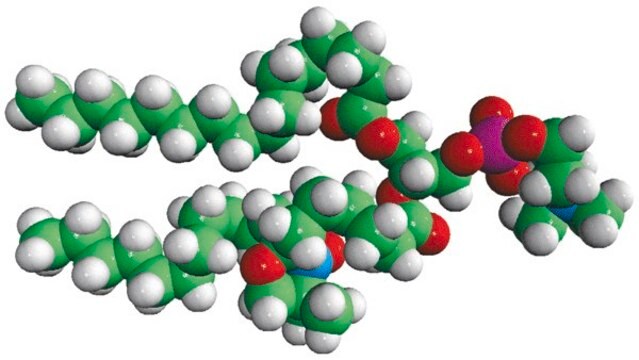
16:0-12 Doxyl PC
Avanti Research™ - A Croda Brand 810600P, powder
Synonym(e):
1-palmitoyl-2-stearoyl-(12-doxyl)-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Assay
>99% (TLC)
Form
powder
Verpackung
pkg of 1 × 1 mg (810600P-1mg)
Hersteller/Markenname
Avanti Research™ - A Croda Brand 810600P
Lipid-Typ
ESR probes
phospholipids
Versandbedingung
dry ice
Lagertemp.
−20°C
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
- as a lipophilic collisional quencher to prepare liposomes used in lipophilic quenching experiments
- to prepare liposomes used in nitroxide quenching experiments to examine the location of each NBD (7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazole) probe in mutants
- as a component in POPC or 1:1 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (POPC)/1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-rac-1-glycerol (POPG) mixtures to prepare unlabelled large unilamellar liposomes
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
Verpackung
Angaben zur Herstellung
Rechtliche Hinweise
auch häufig zusammen mit diesem Produkt gekauft
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Dokumente section.
Wenn Sie Hilfe benötigen, wenden Sie sich bitte an Kundensupport
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.