Wichtige Dokumente
796549
Stahl Aerobic Oxidation TEMPO solution
0.2 M in acetonitrile, Solution for Oxidation of Primary Alcohols
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualitätsniveau
Form
liquid
Eignung der Reaktion
reagent type: oxidant
Konzentration
0.2 M in acetonitrile
Lagertemp.
2-8°C
SMILES String
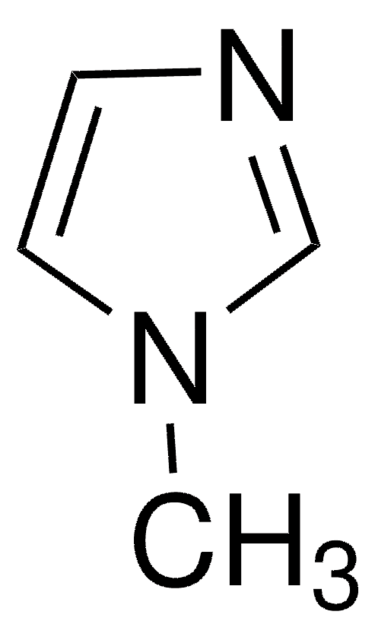
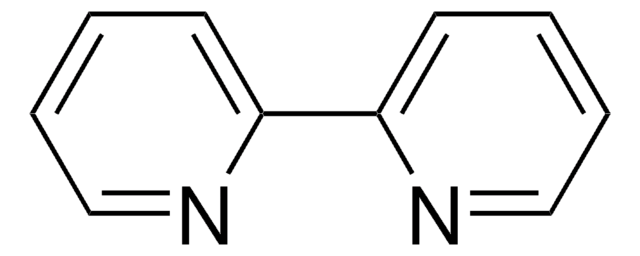
CN1C=CN=C1.CC2(C)CCCC(C)(C)N2[O].C3(C4=NC=CC=C4)=NC=CC=C3
InChI
1S/C10H8N2.C9H18NO.C4H6N2/c1-3-7-11-9(5-1)10-6-2-4-8-12-10;1-8(2)6-5-7-9(3,4)10(8)11;1-6-3-2-5-4-6/h1-8H;5-7H2,1-4H3;2-4H,1H3
InChIKey
BQFURWVGIDXRNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
Ähnliches Produkt
Signalwort
Danger
Gefahreneinstufungen
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Flam. Liq. 2 - Repr. 2 - Skin Corr. 1C
Lagerklassenschlüssel
3 - Flammable liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
35.6 °F
Flammpunkt (°C)
2.0 °C
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Artikel
Alcohol oxidation is one of the most frequently performed oxidation reactions in organic chemistry. The aldehyde and ketone products of alcohol oxidation are useful intermediates en route to complex molecules.
TEMPO (2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidinyloxy or 2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidine 1-oxyl) and its derivatives are stable nitroxy radicals used as catalysts in organic oxidation reactions. TEMPO was discovered by Lebedev and Kazarnovskii in 1960. The stable free radical nature of TEMPO is due to the presence of bulky substituent groups, which hinder the reaction of the free radical with other molecules.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.