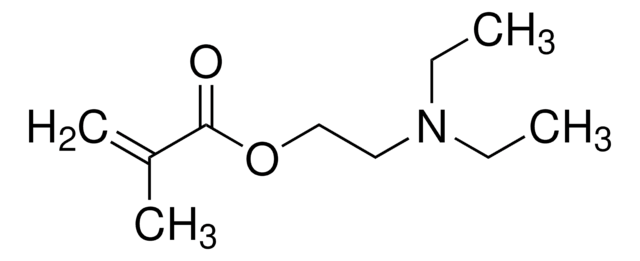
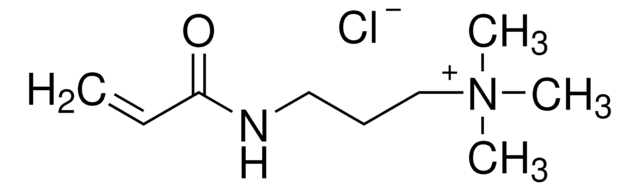
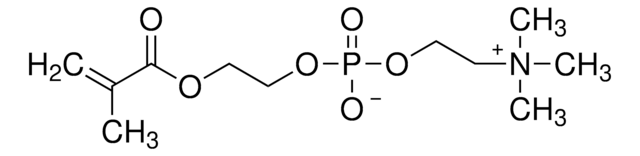
731099
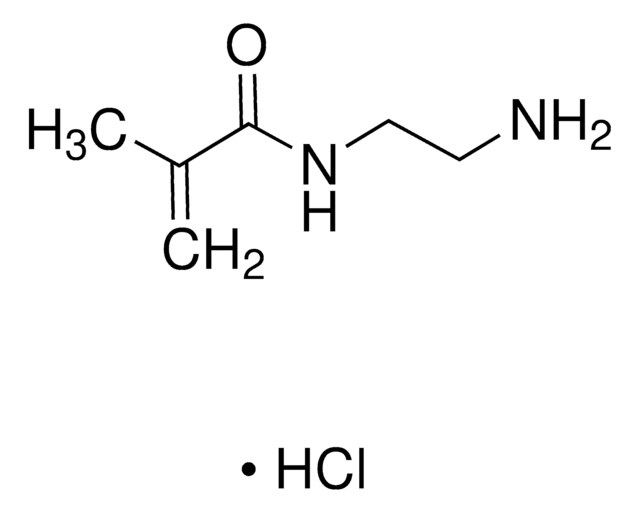
N-(3-Aminopropyl)methacrylamid -hydrochlorid
contains ≤1,000 ppm MEHQ as stabilizer, 98% (HPLC)
Synonym(e):
APMA
Anmeldenzur Ansicht organisationsspezifischer und vertraglich vereinbarter Preise
Alle Fotos(3)
About This Item
Empirische Formel (Hill-System):
C7H14N2O · HCl
CAS-Nummer:
Molekulargewicht:
178.66
MDL-Nummer:
UNSPSC-Code:
12162002
PubChem Substanz-ID:
NACRES:
NA.23
Empfohlene Produkte
Assay
98% (HPLC)
Form
powder
Enthält
≤1,000 ppm MEHQ as stabilizer
mp (Schmelzpunkt)
123-128 °C
Lagertemp.
2-8°C
SMILES String
Cl.CC(=C)C(=O)NCCCN
InChI
1S/C7H14N2O.ClH/c1-6(2)7(10)9-5-3-4-8;/h1,3-5,8H2,2H3,(H,9,10);1H
InChIKey
XHIRWEVPYCTARV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Allgemeine Beschreibung
N-(3-Aminopropyl)methacrylamide hydrochloride (APMA) is an aminoalkyl methacrylamide which can be synthesized by adding 1,3-diaminopropane to 1,3-diaminopropane dihydrogen chloride solution and further mixing the solution with methacrylic anhydride and hydroquinone. It has a primary amine that provides attractive features such as pH-responsiveness, affinity for anionic drugs and conjugation for variety of chemical structures.
Anwendung
APMA can be used in the preparation of copolymers and cross-linked miscellas for gene delivery, drug delivery and diagnostics applications.
Signalwort
Warning
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Eye Irrit. 2
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Efficient RAFT polymerization of N-(3-aminopropyl) methacrylamide hydrochloride using unprotected ?clickable? chain transfer agents
Mendoncca PV, et al.
Reactive and Functional Polymers, 81(2), 1-7 (2014)
Facile synthesis of controlled-structure primary amine-based methacrylamide polymers via the reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer process
Deng Z, et al.
Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 46(15), 4984-4996 (2008)
Gaurasundar M Conley et al.
Nature communications, 10(1), 2436-2436 (2019-06-06)
Thermosensitive microgels are widely studied hybrid systems combining properties of polymers and colloidal particles in a unique way. Due to their complex morphology, their interactions and packing, and consequentially the viscoelasticity of suspensions made from microgels, are still not fully
Polymer mediated peptide immobilization onto amino-containing N-isopropylacrylamide-styrene core-shell particles
Rossi S, et al.
Colloid and Polymer Science, 282(3), 215-222 (2004)
Michika Onoda et al.
Nature communications, 8, 15862-15862 (2017-07-14)
In the field of polymer science, many kinds of polymeric material systems that show a sol-gel transition have been created. However, most systems are unidirectional stimuli-responsive systems that require physical signals such as a change in temperature. Here, we report
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.



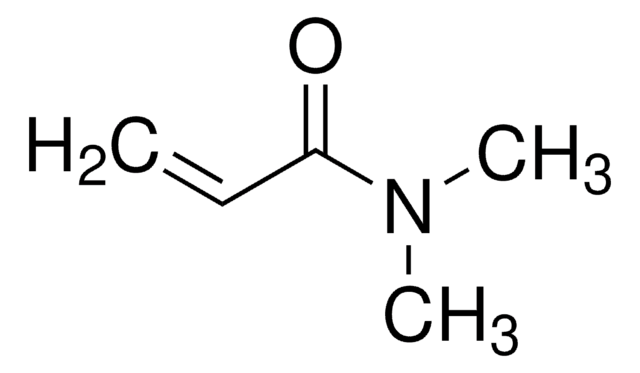
![N-[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]methacrylamid 99%, contains MEHQ as inhibitor](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/295/145/6b4aae15-7cb5-4b7b-9c06-8e6d24e50951/640/6b4aae15-7cb5-4b7b-9c06-8e6d24e50951.png)

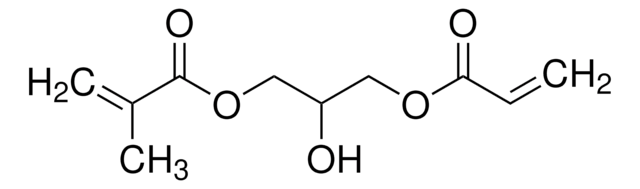
![[3-(Methacryloylamino)propyl]trimethylammoniumchlorid -Lösung 50 wt. % in H2O](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/189/736/089bc8ae-2a98-416d-9f9a-a0a510b6b828/640/089bc8ae-2a98-416d-9f9a-a0a510b6b828.png)