Wichtige Dokumente
283657
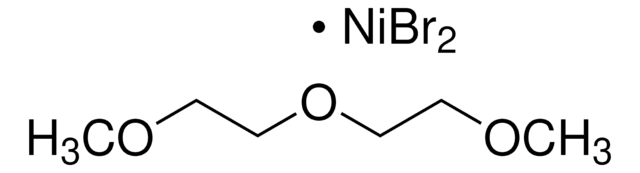
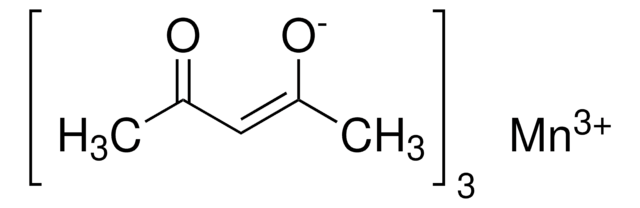
Nickel(II)-acetylacetonat
95%
Synonym(e):
2,4-Pentandion Nickel(II)-Derivat, Ni(acac)2
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Assay
95%
Form
solid
Eignung der Reaktion
core: nickel
reagent type: catalyst
mp (Schmelzpunkt)
230 °C (dec.) (lit.)
SMILES String
CC(=O)\C=C(\C)O[Ni]O\C(C)=C/C(C)=O
InChI
1S/2C5H8O2.Ni/c2*1-4(6)3-5(2)7;/h2*3,6H,1-2H3;/q;;+2/p-2/b2*4-3-;
InChIKey
BMGNSKKZFQMGDH-FDGPNNRMSA-L
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
- Used as a precursor to synthesize Ni-based nanomaterials such as NiO/C nanocomposite and crystalline NiO nanoparticles via different synthetic methods like non-isothermal decomposition and solvothermal method.,·
- Used to prepare Ni catalysts such as Nickel(II) complexes, and hierarchical Ni/beta catalysts for various organictransformations.
- Nickel(II) acetylacetonate has several applications in catalysis: It is used as a catalyst for the polymerization of olefins and transesterification reactions.
- Nickel(II) acetylacetonate can be employed as a catalyst to promote Michael additions.
Ähnliches Produkt
Signalwort
Danger
Gefahreneinstufungen
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Carc. 1A - Muta. 2 - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Sens. 1
Lagerklassenschlüssel
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
428.0 °F
Flammpunkt (°C)
220 °C
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.