SBR00069
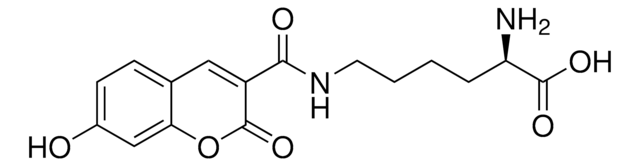
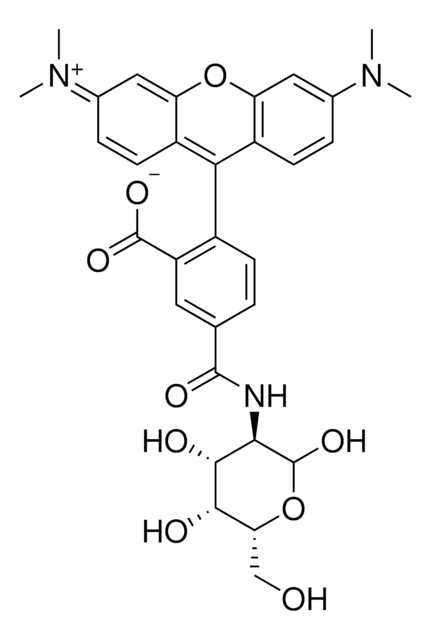
Rhodamine labeled D-Lysine
Suitable for fluorescent microbial imaging
Synonyme(s) :
D-Lysine red, FDAA, TDL
Se connecterpour consulter vos tarifs contractuels et ceux de votre entreprise/organisme
About This Item
Formule empirique (notation de Hill):
C31H34N4O6
Numéro CAS:
Poids moléculaire :
558.62
Code UNSPSC :
12352209
Nomenclature NACRES :
NA.21
Produits recommandés
Description générale
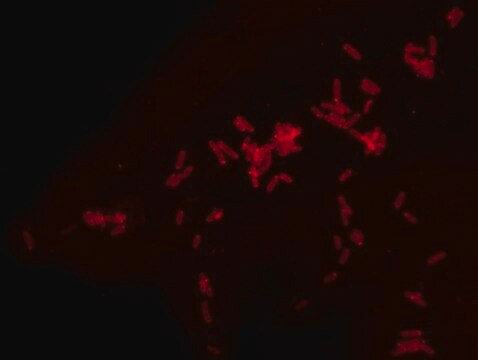
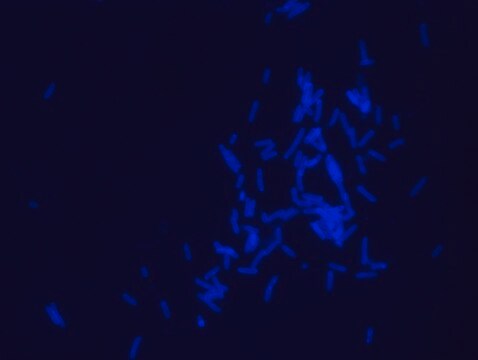
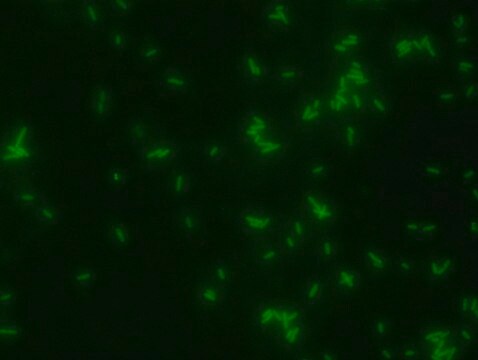
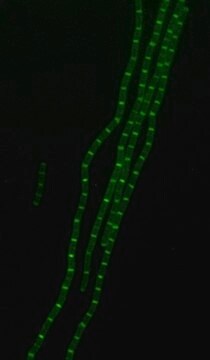
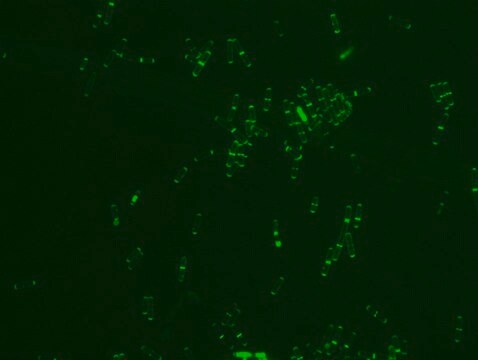
Bacterial Peptidoglycan is a polymer consisting of sugars and amino acids, a mesh-like rigid layer that forms the cell wall. D-Amino Acids (D-AAs) are metabolically incorporated onto the bacterial cell wall by D,D-transpeptidase and/or L,D-transpeptidase. It was recently discovered that those transpeptidases catalyze the metabolic incorporation of exogenous D-AAs with almost no restriction of the side-chain identity. Modification of a D-AA with molecular fluorophores provides fluorescent D-amino acids that can efficiently label in situ peptidoglycan in diverse bacterial species. Rhodamine-Labeled D-lysine (TDL) is a fluorescent derivative of D-lysine that is obtained by a synthetic conjugation of D-lysine to the fluorophore. Rhodamine Labeled D-lysine has high biocompatibility and suitability for labeling peptidoglycans in live bacteria. Additionally, it can be used in tandem with other stains such as FITC-Labeled D-Alanine (SBR00049) to distinguish between different bacteria. Other compatible products useful for live staining include: Rhodamine B Labeled Polymyxin B, FITC Labeled D-Lysine, FITC Labeled Vancomycin and Dansyl Labeled Polymyxin B (SBR00036, SBR00050, SBR00028, SBR00029 and SBR00047).
Application
Fluorescent labeled D-AAs (FDAAs) can be used for many applications including:
- Bacterial cell wall morphology
- Bacterial cell wall formation or remodeling activity
- Bacterial viability/activity
- Identify bacterial activity on surfaces or in substances
- Differentiation between various bacterial strains according to their incorporation profile of different D amino acids and sugars
Remarque sur l'analyse
- Fluorescent microscopy application: Rhodamine Labeled D-lysine has excitation/emission wavelength range at 550/570 nm.
- The recommended working concentration in fluorescent microscopy imaging application is between 250 µM-500 µM in working medium.
- Aliquots of the DMSO solution can be stored at -20 °C, protected from light for at least one month.
Produit(s) apparenté(s)
Réf. du produit
Description
Tarif
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Désolés, nous n'avons pas de COA pour ce produit disponible en ligne pour le moment.
Si vous avez besoin d'assistance, veuillez contacter Service Clients
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Yen-Pang Hsu et al.
Chemical science, 8(9), 6313-6321 (2017-10-11)
Fluorescent d-amino acids (FDAAs) enable efficient in situ labeling of peptidoglycan in diverse bacterial species. Conducted by enzymes involved in peptidoglycan biosynthesis, FDAA labeling allows specific probing of cell wall formation/remodeling activity, bacterial growth and cell morphology. Their broad application
Helene Botella et al.
mBio, 8(5) (2017-09-14)
Peptidoglycan (PG), a polymer cross-linked by d-amino acid-containing peptides, is an essential component of the bacterial cell wall. We found that a fluorescent d-alanine analog (FDAA) incorporates chiefly at one of the two poles in Mycobacterium smegmatis but that polar
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique