G7400
Galactose Oxidase from Dactylium dendroides
lyophilized powder, ≥3,000 units/g solid
Synonyme(s) :
D-Galactose:oxygen 6-oxidoreductase
Se connecterpour consulter vos tarifs contractuels et ceux de votre entreprise/organisme
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
fungus (Dactylium dendroides)
Niveau de qualité
Forme
lyophilized powder
Activité spécifique
≥3,000 units/g solid
Température de stockage
−20°C
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
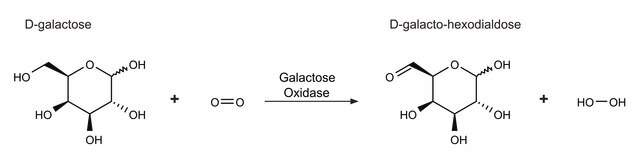
Galactose oxidase is an extracellular copper-containing enzyme, secreted by the deuteromycete fungus Dactylium dendroides. It catalyzes the oxidation of a range of primary alcohols, including D-galactose, to the corresponding aldehyde, with reduction of oxygen to hydrogen peroxide.
Application
Galactose oxidase may be used as an analytical tool for the specific determination of D-galactose in blood plasma, plant extracts, and phospholipids. It could be used for the characterization of terminal D-galactoside units in several polymers.
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Galactose oxidase catalyzes the coversion of D-galactose to D-galacto-hexodialdose.
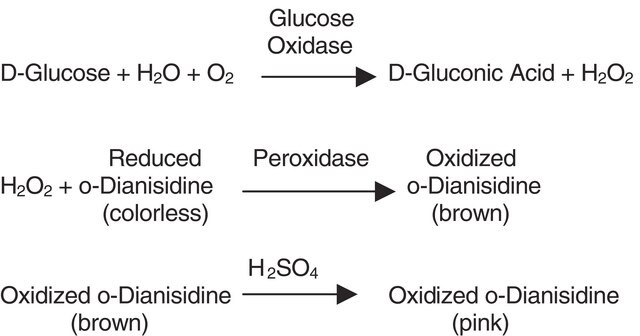
2-Deoxy-D-galactose, lactose, melibiose, raffinose and stachyose react with galactose oxidase in the peroxidase:o-tolidine system.
Essentially no oxidation of D-glucose, L-galactose, L-arabinose or D-glucuronate has been observed.
2-Deoxy-D-galactose, lactose, melibiose, raffinose and stachyose react with galactose oxidase in the peroxidase:o-tolidine system.
Essentially no oxidation of D-glucose, L-galactose, L-arabinose or D-glucuronate has been observed.
Définition de l'unité
One unit will produce a ΔA425 of 1.0 per min at pH 6.0 at 25 °C, in a peroxidase and o-tolidine system. Reaction volume = 3.4 mL. Light path = 1 cm.
Inhibiteur
Réf. du produit
Description
Tarif
Produit(s) apparenté(s)
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Resp. Sens. 1
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 1
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Bei Yue et al.
Frontiers in pharmacology, 12, 774560-774560 (2021-11-20)
Irinotecan (CPT11), a broad-spectrum cytotoxic anticancer agent, induces a series of toxic side-effects. The most conspicuous side-effect is gastrointestinal mucositis, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. A growing body of evidence indicates that bacteria β-glucuronidase (GUS), an enzyme expressed by intestinal
M J McPherson et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 267(12), 8146-8152 (1992-04-25)
The gaoA gene, encoding the secreted copper-containing enzyme galactose oxidase, has been isolated from the Deuteromycete fungus Dactylium dendroides. Degenerate oligonucleotide primers were designed from amino acid sequence data for use in the polymerase chain reaction. A 1.4-kilobase DNA fragment
Takeshi Ito et al.
Talanta, 85(1), 707-712 (2011-06-08)
We proposed a low cost fabrication procedure of a poly(methylmethacrylate) (PMMA) column chip. 3D microchannel structure consisting of four columns in a chip for a mother die was fabricated using dry film photoresist and photolithography technique. Electroforming was applied to
Avgousta Ioannou et al.
Chemical communications (Cambridge, England), 47(40), 11228-11230 (2011-09-15)
Galactose oxidase (GOase) was shown to oxidise several C2/C3 fluorinated galactose analogues. Interestingly, the enzyme was able to distinguish between the 2,3-tetrafluorinated galactose and its epimeric glucose analogue, and this represents the first reported biotransformation of a heavily fluorinated sugar.
Fabio Aparecido Cordeiro et al.
Journal of basic microbiology, 50(6), 527-537 (2010-11-16)
Galactose oxidase (GO) converts galactose to an aldehyde and has several biotechnological applications, including cancer diagnosis. It is mainly produced by Fusarium austroamericanum but is also produced by Fusarium acuminatum and by isolates of the Fusarium graminearum and Gibberella fujikuroi
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique