E5036
Epidermal Growth Factor Protein, human
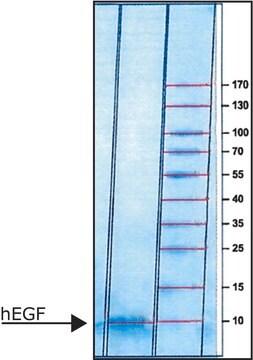
>97% (SDS-PAGE), recombinant, expressed in E. coli, lyophilized powder, suitable for cell culture
Synonyme(s) :
EGF
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Nom du produit
Facteur de croissance épidermique human, EGF, recombinant, expressed in Escherichia coli, >97% (SDS-PAGE)
Source biologique
human
Niveau de qualité
Produit recombinant
expressed in E. coli
Essai
>97% (SDS-PAGE)
Forme
lyophilized powder
Puissance
0.08-0.8 ng/mL EC50
Poids mol.
~6 kDa
Conditionnement
pkg of 200 and 500 μg
Conditions de stockage
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
Impuretés
≤1 EU/μg Endotoxin
Couleur
white
Solubilité
water: soluble 0.190-0.210, clear, colorless
Numéro d'accès UniProt
Température de stockage
−20°C
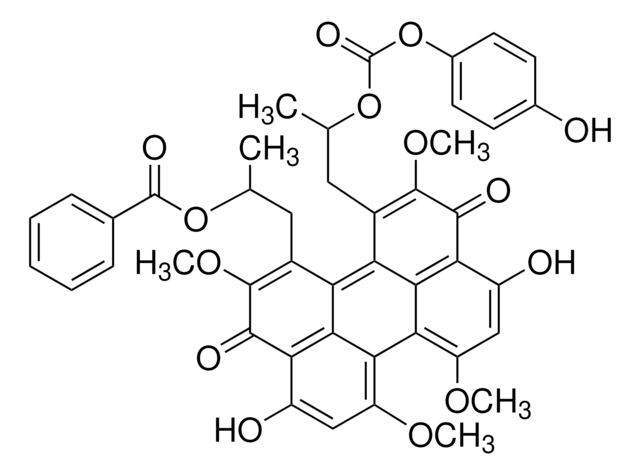
Chaîne SMILES
S(CC[C@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)CNC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)CNC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@H]%12N(CCC%12)C(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](N
InChI
1S/C270H401N73O83S7/c1-24-134(19)217(262(420)293-112-201(355)298-161(69-74-205(359)360)229(387)301-160(45-35-82-286-269(279)280)228(386)333-192(119-428)255(413)307-162(68-73-198(274)352)230(388)316-176(94-141-54-64-150(350)65-55-141)241(399)304-159(44-34-
Clé InChI
GVUGOAYIVIDWIO-UFWWTJHBSA-N
Informations sur le gène
human ... EGF(1950)
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Application
- as a supplement in in LHC-8 medium to culture liver cell lines
- in the fetal bovine serum (FBS)-Dulbecco′s modified essential medium (DMEM) /F12 medium for primary culture of human glioma cells
- as an additive in the conditional medium of normal fibroblasts (NFs) to study its effect on the migration and invasion of endometrial cancer (EC) cells
- as a component in tumorsphere medium
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Formule chimique
2. Gregory, H., Isolation and structure of urogastrone and its relationship to epidermal growth factor. Nature, 257, 325-327 (1975).
3. George-Nascimento, C. et al., Characterization of recombinant human epidermal growth factor produced in yeast. Biochemistry, 27, 797-802 (1988).
4. Todaro, G.J. et al., Transforming growth factors produced by certain human tumor cells: polypeptides that interact with epidermal growth factor receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 77, 5258-5262 (1980).
5. Blomquist, M.C. et al., Vaccinia virus 19-kilodalton protein: relationship to several mammalian proteins, including two growth factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 81, 7363-7367 (1984).
6. Eppstein, D.A. et al., Epidermal growth factor receptor occupancy inhibits vaccinia virus infection. Nature, 318, 663-665 (1985).
Code de la classe de stockage
13 - Non Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 2
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique