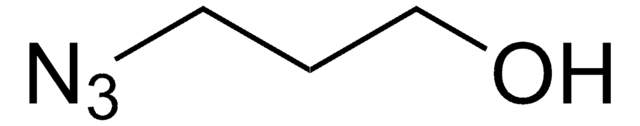
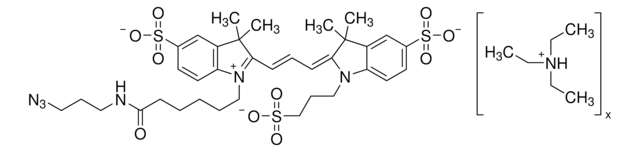
68321
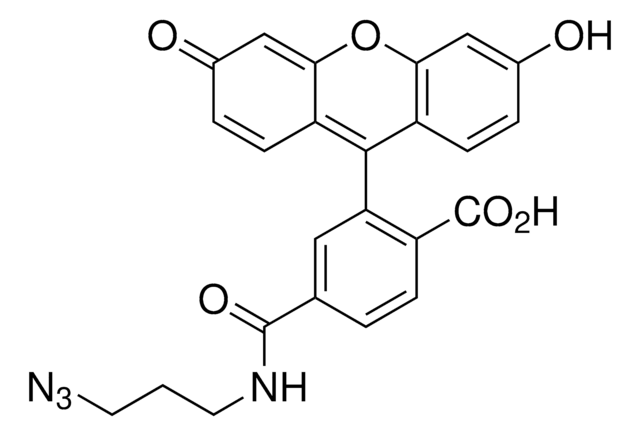
Atto 390 azide
BioReagent, suitable for fluorescence, ≥90% (HPLC)
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Gamme de produits
BioReagent
Niveau de qualité
Essai
≥90% (HPLC)
Forme
solid
Fabricant/nom de marque
ATTO-TEC GmbH
λ
in ethanol (with 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid)
Absorption UV
λ: 380-384 nm Amax
Adéquation
suitable for fluorescence
Température de stockage
−20°C
Chaîne SMILES
CC(CC(C)(C)N1CCCC(NCCOCCOCCOCCN=[N+]=[N-])=O)C2=C1C=C(OC(C=C3C)=O)C3=C2
InChI
1S/C28H41N5O6/c1-20-16-27(35)39-25-18-24-22(17-23(20)25)21(2)19-28(3,4)33(24)9-5-6-26(34)30-7-10-36-12-14-38-15-13-37-11-8-31-32-29/h16-18,21H,5-15,19H2,1-4H3,(H,30,34)
Clé InChI
FEBSRHTZZIMYNR-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Description générale
The azide modification is suitable for reactions with alkyne groups (Huisgen reaction - “Click Chemistry“).
find more information here
Informations légales
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique