41698
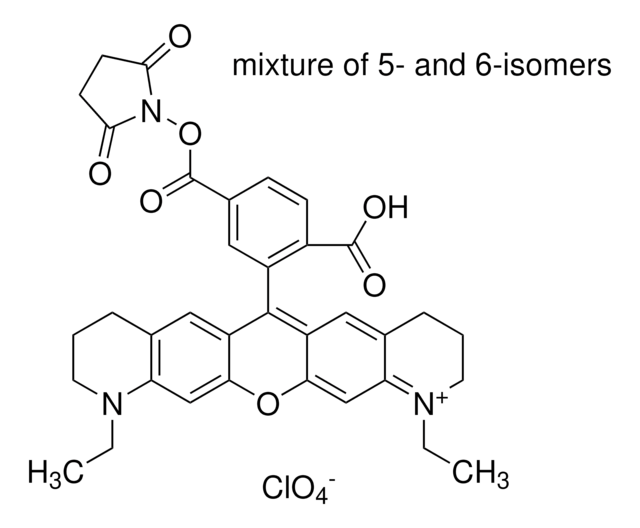
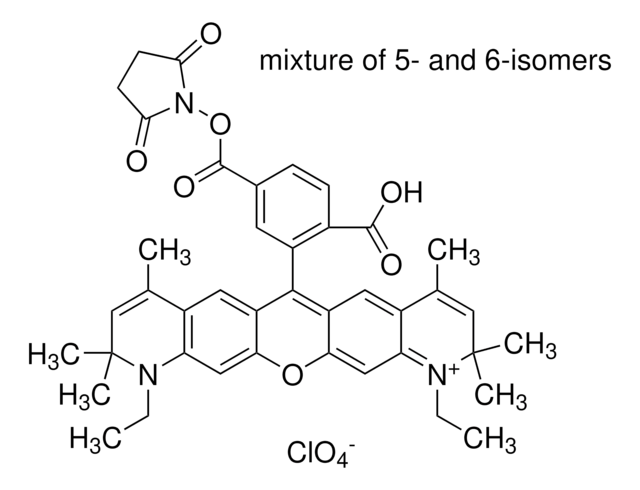
Atto 488 NHS ester
BioReagent, suitable for fluorescence, ≥90% (HPLC)
Synonyme(s) :
Atto 488
Se connecterpour consulter vos tarifs contractuels et ceux de votre entreprise/organisme
About This Item
Code UNSPSC :
12352108
Nomenclature NACRES :
NA.32
Produits recommandés
Gamme de produits
BioReagent
Niveau de qualité
Essai
≥90% (HPLC)
≥90% (degree of coupling)
Fabricant/nom de marque
ATTO-TEC GmbH
λ
in methanol: water (1:1) (with 0.1% perchloric acid)
Absorption UV
λ: 501-507 nm Amax
Adéquation
suitable for fluorescence
Température de stockage
−20°C
Catégories apparentées
Description générale
Atto 488 NHS ester is a hydrophilic fluorescent label with high water solubility. The fluorescence activity is excited efficiently at the 480-515nm range. A suitable excitation source for Atto 488 is the 488 nm line of the Argon-Ion laser.
Application
Atto 488 NHS ester is highly suitable for single-molecule detection applications and high-resolution microscopy such as PALM, dSTORM, and STED. In addition, the dye is used in flow cytometry (FACS) and fluorescence in-situ hybridization (FISH) methods.
Caractéristiques et avantages
Characteristic features of the Atto 488 NHS ester are:
- Strong Absorption.
- High Fluorescence quantum yield.
- High Photostability.
- Excellent water solubility.
Informations légales
This product is for Research use only. In case of intended commercialization, please contact the IP-holder (ATTO-TEC GmbH, Germany) for licensing.
Produit(s) apparenté(s)
Réf. du produit
Description
Tarif
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Analysis of fluorescent nanostructures in biological systems by means of spectral position determination microscopy (SPDM).
Muller, P., et al. et al.
Current Microscopy Contributions to Advances in Science and Technology, 1, 3-12 (2012)
Qian Peter Su et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 117(26), 15036-15046 (2020-06-17)
Mammalian DNA replication is initiated at numerous replication origins, which are clustered into thousands of replication domains (RDs) across the genome. However, it remains unclear whether the replication origins within each RD are activated stochastically or preferentially near certain chromatin
Switching modulation for protein labeling with activatable fluorescent probes.
Kalyan K Sadhu et al.
Chembiochem : a European journal of chemical biology, 12(9), 1299-1308 (2011-06-02)
Christiane Iserman et al.
Molecular cell, 80(6), 1078-1091 (2020-12-09)
We report that the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein (N-protein) undergoes liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) with viral RNA. N-protein condenses with specific RNA genomic elements under physiological buffer conditions and condensation is enhanced at human body temperatures (33°C and 37°C) and reduced
Gražvydas Lukinavičius et al.
Current opinion in chemical biology, 15(6), 768-774 (2011-11-15)
Numerous synthetic fluorophores have been developed that can switch their spectroscopic properties upon interaction with other molecules or by irradiation with light. In recent years, protein-labeling techniques have been introduced that permit the specific attachment of such molecules to proteins
Articles
Fluorescent Labeling of Peptides
Fluorescent Labeling of Peptides
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique