F0048000
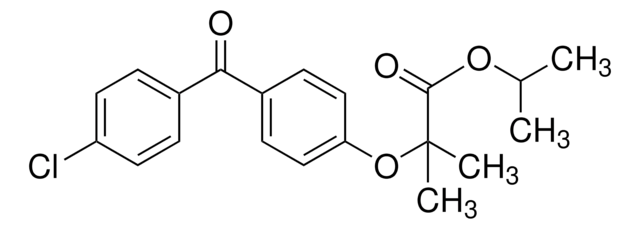
Fenofibrate
European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard
Synonyme(s) :
2-[4-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoic acid isopropyl ester
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Qualité
pharmaceutical primary standard
Fabricant/nom de marque
EDQM
Technique(s)
HPLC: suitable
gas chromatography (GC): suitable
Application(s)
pharmaceutical
Format
neat
Chaîne SMILES
CC(C)OC(=O)C(C)(C)Oc1ccc(cc1)C(=O)c2ccc(Cl)cc2
InChI
1S/C20H21ClO4/c1-13(2)24-19(23)20(3,4)25-17-11-7-15(8-12-17)18(22)14-5-9-16(21)10-6-14/h5-13H,1-4H3
Clé InChI
YMTINGFKWWXKFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Informations sur le gène
human ... PPARA(5465)
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Conditionnement
Autres remarques
Produit(s) apparenté(s)
Mention d'avertissement
Warning
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
STOT RE 2 Oral
Organes cibles
Liver
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 1
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Service Clients
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique