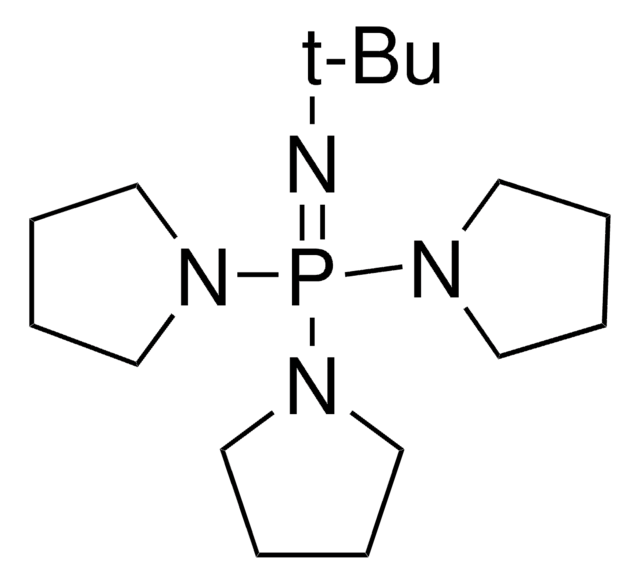
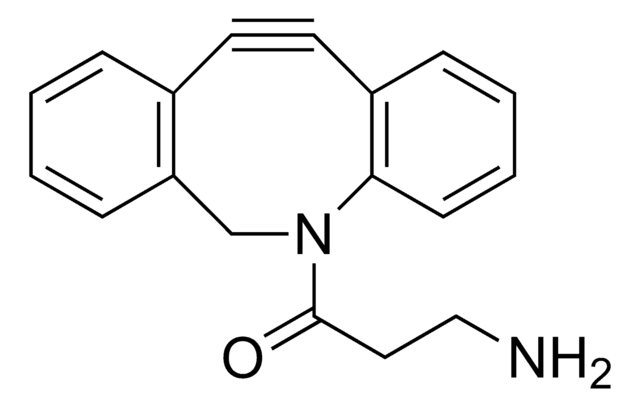
906301
BTTES
Synonyme(s) :
3-(4-((Bis((1-(tert-butyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)amino)methyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonic acid, Copper click-chemistry ligand, Water-soluble CuAAC ligand
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Forme
solid
Capacité de réaction
reaction type: click chemistry
Disponibilité
available only in USA
Température de stockage
2-8°C
Catégories apparentées
Application
Produit(s) apparenté(s)
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Self-react. C
Code de la classe de stockage
5.2 - Organic peroxides and self-reacting hazardous materials
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Vous ne trouvez pas la bonne version ?
Si vous avez besoin d'une version particulière, vous pouvez rechercher un certificat spécifique par le numéro de lot.
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique
![Tris[(1-benzyl-1H-1, 2, 3-triazol-4-yl)methyl]amine 97%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/179/695/86a721c8-2a4c-4e4f-bc36-6276ce7a941f/640/86a721c8-2a4c-4e4f-bc36-6276ce7a941f.png)
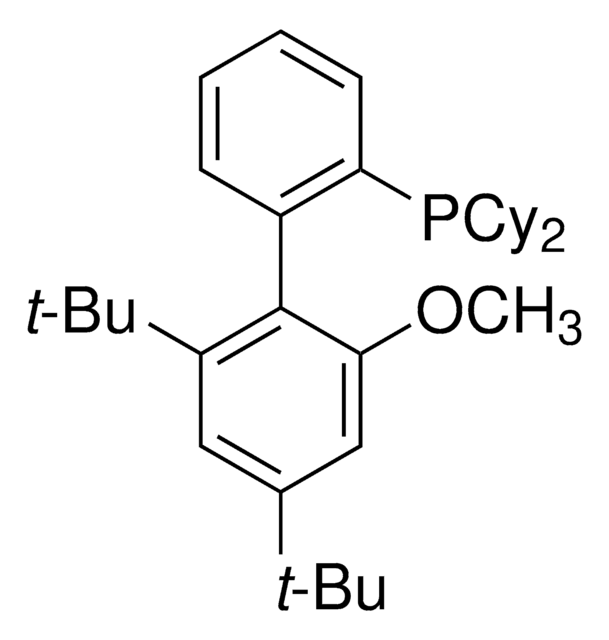
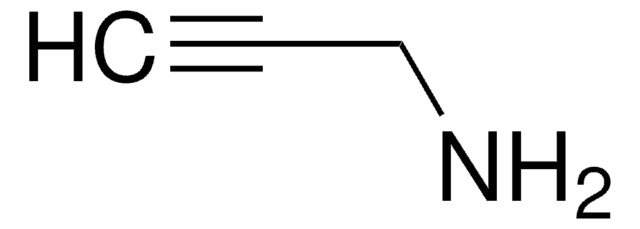

![Tetrakis[tris(dimethylamino)phosphoranylidenamino]phosphonium chloride 95%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/160/963/9dd6d457-17b2-44dc-8ea2-d3c0475b3664/640/9dd6d457-17b2-44dc-8ea2-d3c0475b3664.png)