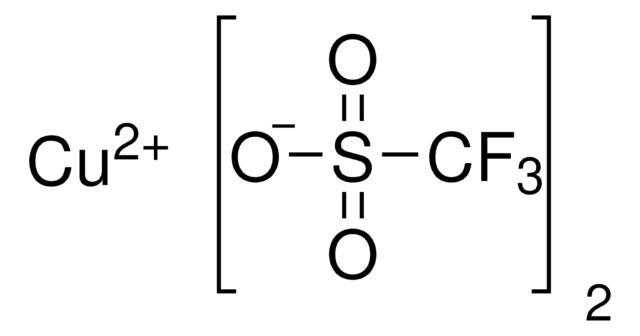796549
Stahl Aerobic Oxidation TEMPO solution
0.2 M in acetonitrile, Solution for Oxidation of Primary Alcohols
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Forme
liquid
Pertinence de la réaction
reagent type: oxidant
Concentration
0.2 M in acetonitrile
Température de stockage
2-8°C
Chaîne SMILES
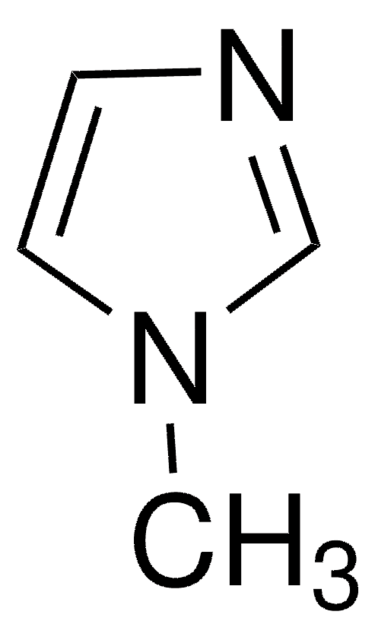
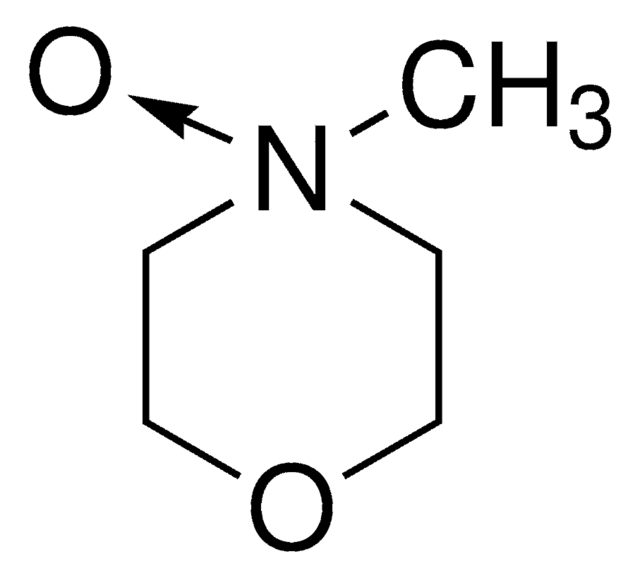
CN1C=CN=C1.CC2(C)CCCC(C)(C)N2[O].C3(C4=NC=CC=C4)=NC=CC=C3
InChI
1S/C10H8N2.C9H18NO.C4H6N2/c1-3-7-11-9(5-1)10-6-2-4-8-12-10;1-8(2)6-5-7-9(3,4)10(8)11;1-6-3-2-5-4-6/h1-8H;5-7H2,1-4H3;2-4H,1H3
Clé InChI
BQFURWVGIDXRNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Description générale
Application
Produit(s) apparenté(s)
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Classification des risques
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Flam. Liq. 2 - Repr. 2 - Skin Corr. 1C
Code de la classe de stockage
3 - Flammable liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
35.6 °F
Point d'éclair (°C)
2.0 °C
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
Alcohol oxidation is one of the most frequently performed oxidation reactions in organic chemistry. The aldehyde and ketone products of alcohol oxidation are useful intermediates en route to complex molecules.
TEMPO (2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidinyloxy or 2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidine 1-oxyl) and its derivatives are stable nitroxy radicals used as catalysts in organic oxidation reactions. TEMPO was discovered by Lebedev and Kazarnovskii in 1960. The stable free radical nature of TEMPO is due to the presence of bulky substituent groups, which hinder the reaction of the free radical with other molecules.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique
![9-Azabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane N-oxyl 95%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/287/155/e2f4a2e1-1d4e-4bed-9187-9e16d23cbbbf/640/e2f4a2e1-1d4e-4bed-9187-9e16d23cbbbf.png)
![1,8-Diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undéc-7-ène 98%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/120/564/5b373e23-1624-489c-8efb-692de0f96ffb/640/5b373e23-1624-489c-8efb-692de0f96ffb.png)