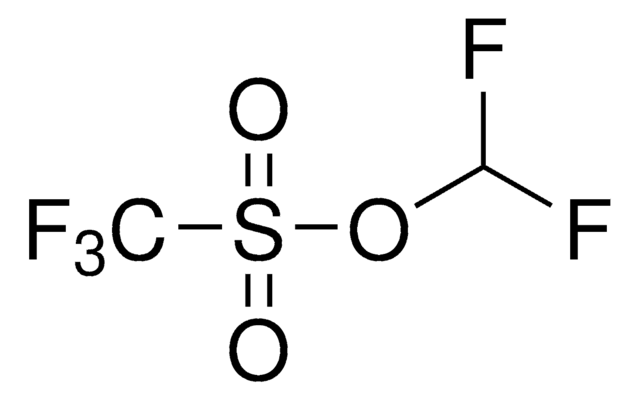
767840
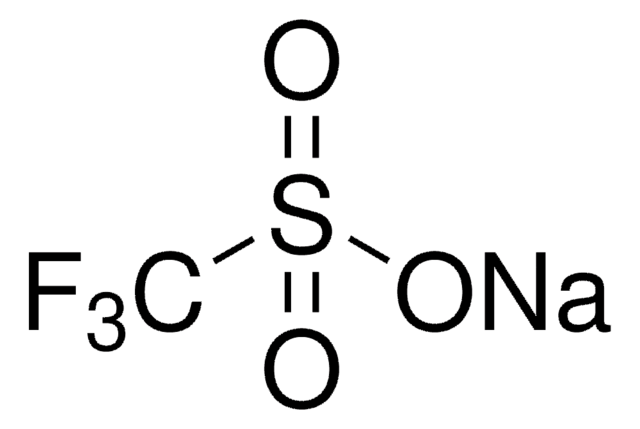
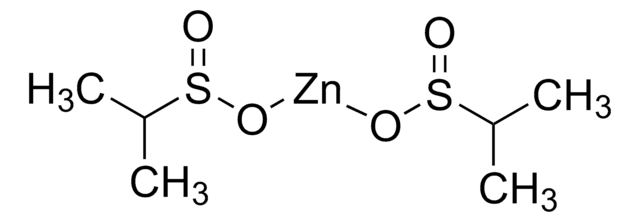
Zinc difluoromethanesulfinate
95%
Synonyme(s) :
Bis(((difluoromethyl)sulfinyl)oxy)zinc, 1,1-difluoro-methanesulfinic acid zinc salt (2:1), Baran difluoromethylation reagent, DFMS
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Essai
95%
Forme
solid
Capacité de réaction
reaction type: C-C Bond Formation
reaction type: Fluorinations
Pertinence de la réaction
reagent type: catalyst
reaction type: C-H Activation
reagent type: diversification reagent
Groupe fonctionnel
fluoro
sulfinic acid
Température de stockage
2-8°C
Chaîne SMILES
FC(F)S(=O)O[Zn]OS(=O)C(F)F
InChI
1S/2CH2F2O2S.Zn/c2*2-1(3)6(4)5;/h2*1H,(H,4,5);/q;;+2/p-2
Clé InChI
UGEYAPVLXKEKMP-UHFFFAOYSA-L
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Application
Practical and Innate Carbon-Hydrogen Functionalization of Heterocycles
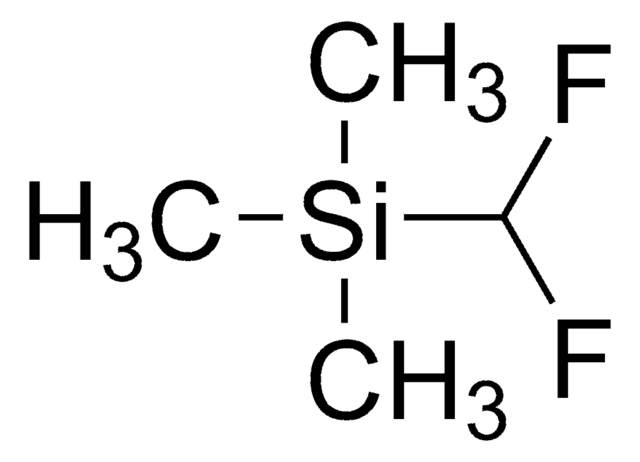
DFMS is a new reagent for direct difluoromethylation of organic substrates via a radical process. This mild, operationally simple, chemoselective, and scalable difluoromethylation method is compatible with a range of nitrogen-containing heteroarene substrates of varying complexity as well as select classes of conjugated p−systems and thiols.†
A New Reagent for Direct Difluoromethylation
Learn More at the Professor and Product Portal of Professor Phil S. Baran.
Liaison
Mention d'avertissement
Warning
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Organes cibles
Respiratory system
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
The synthesis of heteroaromatic and aromatic compounds is at the heart of the chemical industry. The ever-growing demand for new chemical entities, coupled with dwindling resources and time constraints allotted to any given research project, a rapid way to diversify (hetero)aromatic scaffolds is needed.
The synthesis of heteroaromatic and aromatic compounds is at the heart of the chemical industry. The ever-growing demand for new chemical entities, coupled with dwindling resources and time constraints allotted to any given research project, a rapid way to diversify (hetero)aromatic scaffolds is needed.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique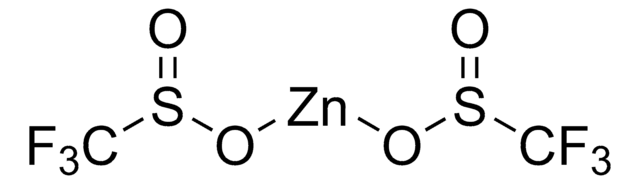

![Zinc di[bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide] 95%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/336/073/952daadd-0a7c-4bec-bbaf-442a24c62161/640/952daadd-0a7c-4bec-bbaf-442a24c62161.png)