S7115
ApopTag Positive Control Slides, rat mammary gland 4d post weaning
This product is intended as a positive control for use with all ApopTag In Situ Apoptosis Detection Kits.
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12161503
eCl@ss:
32161000
NACRES:
NA.32
Recommended Products
Quality Level
manufacturer/tradename
ApopTag
Chemicon®
technique(s)
activity assay: suitable (apoptosis)
shipped in
ambient
General description
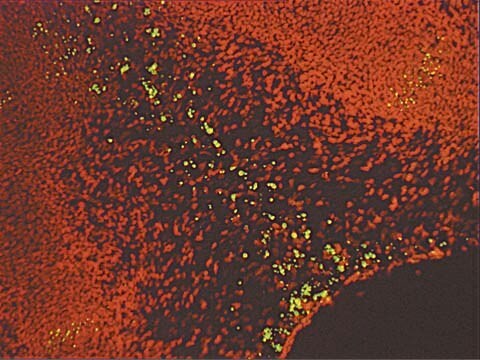
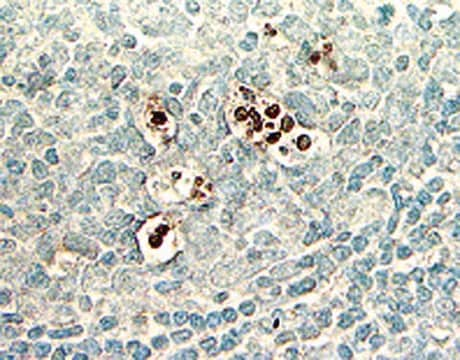
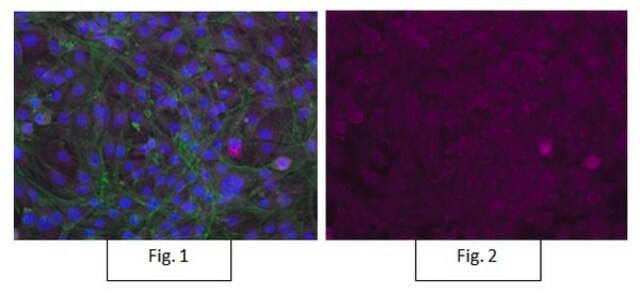
Rat mammary gland undergoes programmed cell death processes during the tissue regression that follows lactation. Apoptotic bodies, which can be seen by routine histologic staining, can be specifically stained by techniques that localize DNA strand breaks in situ. The specificity of staining for strand breaks can thus be correlated with the morphological changes that define the process of apoptosis.
This product is intended as a positive control for use with all ApopTag In Situ Apoptosis Detection Kits. These reference slides are also useful as teaching aides, and for procedural troubleshooting. Each pack of ApopTag Control Slides contains 5 unstained positive control slides. Rat mammary glands were obtained at the fourth day after weaning and were fixed for 18 hours in 10% neutral buffered formalin. After embedding in paraffin, 5 μm thick sections were cut from the middle of the tissue and were mounted on silanized slides.
Application
Interpretation of Staining
These positive control slides of female rat mammary tissue 4-days post weaning show only 1-2% of the cells being apoptotic. Microscopic inspection is usually required to confirm proper kit activity.
Stain is generally localized to chromatin, and is intensely colored. The localization and sensitivity to be expected with the ApopTag Peroxidase (S7100, S7101) or ApopTag Fluorescein (S7110, S7111, S7160, S7165) Kits are similar. Positive objects vary in size, from intact nuclei to much smaller apoptotic bodies, and in shape, from round to irregular. Such objects may be either isolated, clustered, or engulfed in the cytoplasm of a phagocytic cell. Some unstained apoptotic nuclei or bodies may also be expected. Light cytoplasmic staining might co-localize with intense chromatin staining (this might be due to fragmented DNA leaching from the nucleus, or that in phagocytic organelles). If staining of non-apoptotic cell nuclei is observed with the ApopTag Peroxidase kits (S7100, S7101), the user can attempt to decrease the substrate development time or temperature, or to further dilute the anti-digoxigenin antibody reagent in 0.5% (w:v) BSA. Counterstaining is recommended (see The Complete ApopTag Manual).
Limitations
This control tissue has been selected for positive staining with all ApopTag Kits. Results with control tissue may vary from results with other tissues because of both sample preparation differences and intrinsic tissue differences.
These positive control slides of female rat mammary tissue 4-days post weaning show only 1-2% of the cells being apoptotic. Microscopic inspection is usually required to confirm proper kit activity.
Stain is generally localized to chromatin, and is intensely colored. The localization and sensitivity to be expected with the ApopTag Peroxidase (S7100, S7101) or ApopTag Fluorescein (S7110, S7111, S7160, S7165) Kits are similar. Positive objects vary in size, from intact nuclei to much smaller apoptotic bodies, and in shape, from round to irregular. Such objects may be either isolated, clustered, or engulfed in the cytoplasm of a phagocytic cell. Some unstained apoptotic nuclei or bodies may also be expected. Light cytoplasmic staining might co-localize with intense chromatin staining (this might be due to fragmented DNA leaching from the nucleus, or that in phagocytic organelles). If staining of non-apoptotic cell nuclei is observed with the ApopTag Peroxidase kits (S7100, S7101), the user can attempt to decrease the substrate development time or temperature, or to further dilute the anti-digoxigenin antibody reagent in 0.5% (w:v) BSA. Counterstaining is recommended (see The Complete ApopTag Manual).
Limitations
This control tissue has been selected for positive staining with all ApopTag Kits. Results with control tissue may vary from results with other tissues because of both sample preparation differences and intrinsic tissue differences.
Quality
ApopTag Control Slides have been qualified for use with all ApopTag Kits.
Storage and Stability
Recommended Storage 18°C to 25°C.
Legal Information
CHEMICON is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Local exposure of 849 MHz and 1763 MHz radiofrequency radiation to mouse heads does not induce cell death or cell proliferation in brain.
Kim, TH; Kim, TH; Huang, TQ; Jang, JJ; Kim, MH; Kim, HJ; Lee, JS; Pack, JK; Seo, JS; Park, WY
Experimental & Molecular Medicine null
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service