S7101
ApopTag Plus Peroxidase In Situ Apoptosis Kit
The ApopTag Plus Peroxidase In Situ Apoptosis Detection Kit detects apoptotic cells by labeling & detecting DNA strand breaks by the indirect TUNEL method.
Synonym(s):
In Situ Apoptosis Detection Kit
About This Item
Recommended Products
General description
The ApopTag Peroxidase Kits have been qualified for use in histochemical and cytochemical staining of the following specimens: formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues, cryostat sections, cell suspensions, cytospins, and cell cultures. Whole mount-methods have been developed (34, 45). (See datasheet Sec. V. for References).
The staining specificity of the ApopTag Peroxidase Kits has been demonstrated by Chemicon and many other laboratories. Chemicon has tested many types of model cell and tissue systems, including: (a) human prostate, thymus, and large intestine (in-house data); (b) rat ventral prostate post-castration (21), (c) rat thymus lymphocytes treated in vitro with dexamethasone (3, 13), (d) 14-day mouse embryo limbs (1) and (e) rat mammary gland in regression after weaning (36). In the thymocyte and prostate models, agarose gel electrophoresis was used to assess the amount of DNA laddering, which peaked coincidentally with the maximum percentage of stained cells. Numerous journal publications from laboratories worldwide have established the usefulness of ApopTag Kits. (See datasheet Sec. V. References, Publications Citing ApopTag Kits).
Application
ApopTag In Situ Apoptosis Detection Kits label apoptotic cells in research samples by modifying DNA fragments utilizing terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) for detection of apoptotic cells by specific staining.
This manual contains information and protocols for the ApopTag Plus In Situ Apoptosis Detection Kit.
Principles of the Procedure
The reagents provided in ApopTag Peroxidase Kits are designed to label the free 3′OH DNA termini in situ with chemically labeled and unlabeled nucleotides. The nucleotides contained in the Reaction Buffer are enzymatically added to the DNA by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) (13, 31). TdT catalyzes a template-independent addition of nucleotide triphosphates to the 3′-OH ends of double-stranded or single-stranded DNA. The incorporated nucleotides form an oligomer composed of digoxigenin-conjugated nucleotide and unlabeled nucleotide in a random sequence. The ratio of labeled to unlabeled nucleotide in ApopTag Peroxidase Kits is optimized to promote anti-digoxigenin antibody binding. The exact length of the oligomer added has not been measured.
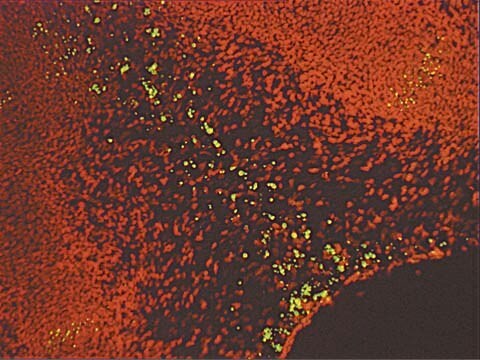
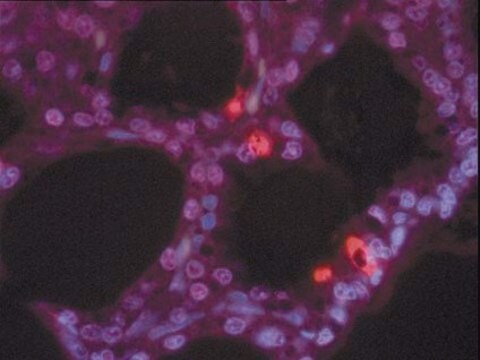
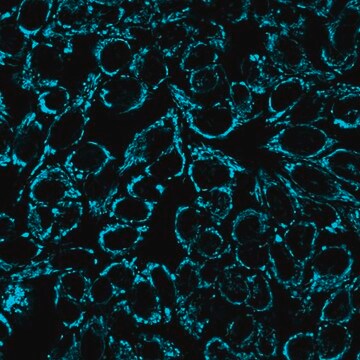
DNA fragments which have been labeled with the digoxigenin-nucleotide are then allowed to bind an anti-digoxigenin antibody that is conjugated to a peroxidase reporter molecule (Figure 1A). The bound peroxidase antibody conjugate enzymatically generates a permanent, intense, localized stain from chromogenic substrates, providing sensitive detection in immunohistochemistry or immunocytochemistry (i.e. on tissue or cells). This mixed molecular biological-histochemical systems allows for sensitive and specific staining of very high concentrations of 3′-OH ends that are localized in apoptotic bodies.
The ApopTag system differs significantly from previously described in situ labeling techniques for apoptosis (13, 16, 38, 46), in which avidin binding to cellular biotin can be a source of error. The digoxigenin/anti-digoxigenin system has been found to be equally sensitive to avidin/biotin systems (22). The sole natural source of digoxigenin is the digitalis plant. Immunochemically-similar ligands for binding of the anti-digoxigenin antibody are generally insignificant in animal tissues, ensuring low background staining. Affinity purified sheep polyclonal antibody is the specific anti-digoxigenin reagent used in ApopTag Kits. This antibody exhibits <1% cross-reactivity with the major vertebrate steroids. In addition, the Fc portion of this antibody has been removed by proteolytic digestion to eliminate any non-specific adsorption to cellular Fc receptors.
Results using ApopTag Kits have been widely published (see Sec. V. References, Publications Citing ApopTag Kits). The ApopTag product line provides various options in experimental design. A researcher can choose to detect staining by brightfield or fluorescence microscopy or by flow cytometry, depending on available expertise and equipment. There are also opportunities to study other proteins of interest in the context of apoptosis when using ApopTag Kits. By using antibodies conjugated with an enzyme other than peroxidase and an appropriate choice of substrate, it is possible to simultaneously examine another protein and apoptosis using ApopTag Peroxidase Kits.
Components
Reaction Buffer 91417 2.0 mL -15°C to -25°C
TdT Enzyme 90418 0.672 mL -15°C to -25°C
Stop/Wash Buffer 90419 20 mL -15°C to -25°C
Anti-Digoxigenin-Peroxidase* 90420 3.0 mL 2°C to 8°C
Plastic Coverslips 90421 100 ea. Room Temp.
Control Slides 90422 2 each Room Temp.
DAB Substrate 90423 130 μL 2°C to 8°C
DAB Dilution Buffer 90424 6.5 mL 2°C to 8°C
*affinity purified sheep polyclonal antibody
Number of samples per kit: Sufficient materials are provided to stain 40 tissue specimens of approximately 5 cm2 each when used according to instructions. Reaction Buffer will be fully consumed before other reagents when kits are used for slide-mounted specimens.
Storage and Stability
Precautions
1. The following kit components contain potassium cacodylate (dimethylarsinic acid) as a buffer: Equilibration Buffer (90416), Reaction Buffer (90417), and TdT Enzyme (90418). These components are harmful if swallowed; avoid contact with skin and eyes (wear gloves, glasses) and wash areas of contact immediately.
2. DAB (3,3′ diaminobenzidine) Substrate (90423) has been demonstrated to be a potential carcinogen and skin contact should be avoided. If skin contact does occur, flush with copious amounts of dH2O.
3. Antibody Conjugates (90420) contains 0.08% sodium azide as a preservative.
4. TdT Enzyme (90418) contains glycerol and will not freeze at -20°C. For maximum shelf life, do not warm this reagent to room temp. before dispensing.
Legal Information
Disclaimer
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Chronic 2 - Carc. 1B - Muta. 2 - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT RE 2 Inhalation
Target Organs
Respiratory Tract
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Cellular apoptosis assays to detect programmed cell death using Annexin V, Caspase and TUNEL DNA fragmentation assays.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service