SCP0152
Gastrin I (1-14)
≥92% (HPLC)
Se connecterpour consulter vos tarifs contractuels et ceux de votre entreprise/organisme
About This Item
Formule empirique (notation de Hill) :
C79H100N16O27
Poids moléculaire :
1705.73
Code UNSPSC :
51111800
Nomenclature NACRES :
NA.32
Produits recommandés
Essai
≥92% (HPLC)
Forme
lyophilized
Composition
Peptide Content, ≥75%
Conditions de stockage
protect from light
Température de stockage
−20°C
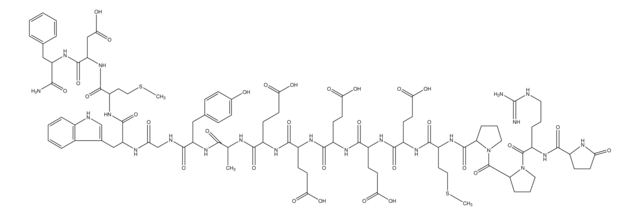
Amino Acid Sequence
Glp-Gly-Pro-Trp-Leu-Glu-Glu-Glu-Glu-Glu-Ala-Tyr-Gly-Trp
Description générale
Gastrin, a classic digestive hormone, is found in three major forms: gastrin-34 (big gastrin), gastrin-17 (little gastrin), and gastrin-13 (minigastrin). Mammalian gastrin consists of a C-terminal four amino-acid sequence and a sulfated tyrosine 7 residue from the C-terminus. Gastrin is mostly found in the G cells of the stomach mucosa. Nutrients and gastrin-releasing peptides stimulate the release of gastrin.
Application
Gastrin I (1-14) has been used:
- as a component of gastric cancer stem/progenitor cell (GCSPC) medium for tumorsphere culture
- as a supplement in organoid growth medium (OGM) for patient-derived organoid (PDO)
- in viable lymphocytes culture for re-stimulation assay
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Gastrin is a linear polypeptide that induces the secretion of gastric acid (HCl) by parietal cells.
The peptide gastrin I (1-14), which lacks a basic site, forms positive ions. Gastrin promotes the production and liberation of histamine in enterochromaffin-like cells through cholecystokinin 2 receptor (CCK2R). It also stimulates the release of gastric acid in parietal cells via the CCK2R receptor. Gastrin plays a key role in Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. It may play a role in the development of colorectal carcinoma.
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Vous ne trouvez pas la bonne version ?
Si vous avez besoin d'une version particulière, vous pouvez rechercher un certificat spécifique par le numéro de lot.
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
C M Thorburn et al.
Gastroenterology, 115(2), 275-280 (1998-07-25)
Gastrin is a putative promoter of colorectal carcinomas. The aim of this study was to evaluate the temporal relationship between gastrinemia and development of colorectal malignancy. We conducted a nested case-control study among 128,992 subscribers to a health maintenance program
Zhi-Feng Miao et al.
Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio), 32(12), 3062-3074 (2014-08-22)
Peritoneal dissemination is the most common cause of death in gastric cancer patients. The hypoxic microenvironment plays a major role in controlling the tumor stem cell phenotype and is associated with patients' prognosis through hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), a key transcriptional
Nicholas Osborne et al.
Cancer immunology, immunotherapy : CII, 68(10), 1635-1648 (2019-09-25)
Pancreatic cancer has been termed a 'recalcitrant cancer' due to its relative resistance to chemotherapy and immunotherapy. This resistance is thought to be due in part to the dense fibrotic tumor microenvironment and lack of tumor infiltrating CD8 + T cells. The
Junjie Gao et al.
Rapid communications in mass spectrometry : RCM, 22(24), 4066-4072 (2008-11-21)
Negative ion production from peptides and proteins was investigated by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry. Although most research on peptide and protein identification with ionization by MALDI has involved the detection of positive ions, for some acidic peptides
F L Lai Benjamin et al.
Advanced functional materials, 30(48) (2021-03-12)
Tumor progression relies heavily on the interaction between the neoplastic epithelial cells and their surrounding stromal partners. This cell cross-talk affects stromal development, and ultimately the heterogeneity impacts drug efflux and efficacy. To mimic this evolving paradigm, we have micro-engineered
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique
![[Leu15]-gastrine I humaine ≥95% (HPLC)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/153/342/d4cb3dd7-13f1-46cf-8d1f-3907a5de7a83/640/d4cb3dd7-13f1-46cf-8d1f-3907a5de7a83.png)