Description générale
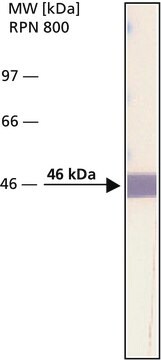
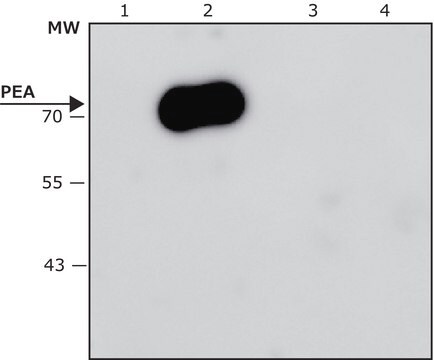
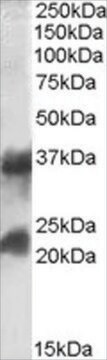
Recombinant DNA technology enables the insertion of specific short sequences into genes of interest. This can provide an ′affinity handles′ (tags) for the selective identification and purification of the recombinant protein.1-3 The addition of Bacterial Alkaline Phosphatase tag to a given gene, creates stable fusion product that does not appear to interfere with the bioactivity of the protein, or with the biodistribution of the Bacterial Alkaline Phosphatase tagged product. Bacterial Alkaline Phosphatase (also known as PhoA, EC 3.1.3.1) is a app. ∼50 kDa protein, derived from E.coli.
Spécificité
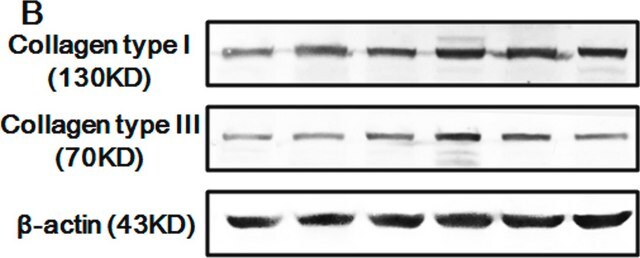
Monoclonal Anti-BAP antibody specifically recognizes Bacterial Alkaline Phosphatase-tagged fusion protein.
Application
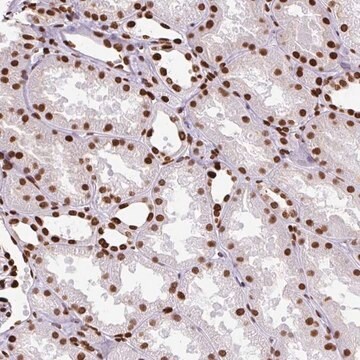
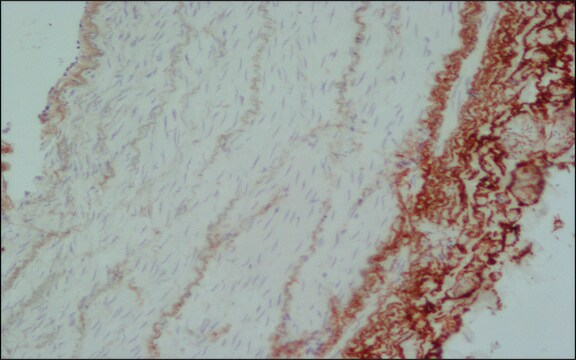
Monoclonal Anti-Bacterial Alkaline Phosphatase antibody may be useful in various immunotechniques, to identify the expression of Bacterial Alkaline Phosphatase fusion protein in situ or by immunoblotting, in bacteria, bacterial lysates, and cells or tissues transfected with Bacterial Alkaline Phosphatase fusion protein expressing vectors. In addition, expression system that exploits the Bacterial Alkaline Phosphatase signal sequence in order to translocate a target protein to the periplasm, may be used to evaluate how changes in the composition and sequence of amino acids near the Bacterial Alkaline Phosphatase-target protein junction influence the periplasmic accumulation of the target recombinant protein.8
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Alkaline phosphatase appears to require export to the periplasm for its enzymatic activity.4 Fusions of the secreted alkaline phosphatase to an integral cytoplasmic membrane protein of E.coli shows different activities depending on where is it fused with the membrane protein.5 Fusions to positions in or near the periplasmic (extracellular) domain lead to high alkaline phosphatase activity, whereas those located to positions in the cytoplasmic domain reside in low activity. Consequently, analysis of alkaline phosphatase fusions to membrane proteins of unknown structure are generally useful in determining their membrane topologies.4 Expression of enzymatically active protein fusions in E.coli could facilitate the analysis of proteins and even replace some reagents frequently used in immunology such as chemically-produced antibody-enzyme conugates.6,7
Forme physique
Supplied as a solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline pH 7.4, containing 15 mM sodium azide as a preservative.
Stockage et stabilité
For continuous use, store at 2-8 °C for up to one month. For extended storage, freeze in working aliquots. Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. If slight turbidity occurs upon prolonged storage, clarify the solution by centrifugation before use. Working dilution samples should be discarded if not used within 12 hours.
Clause de non-responsabilité
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.