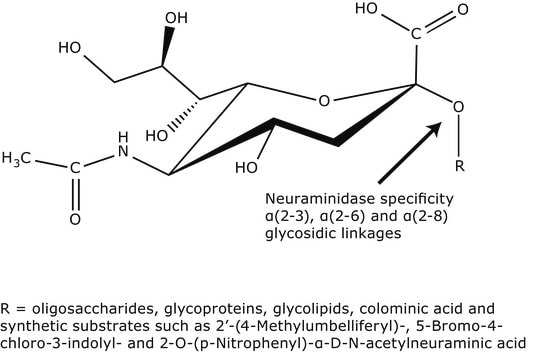
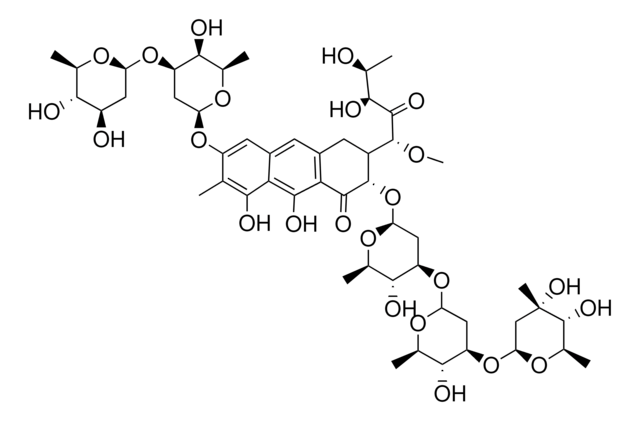
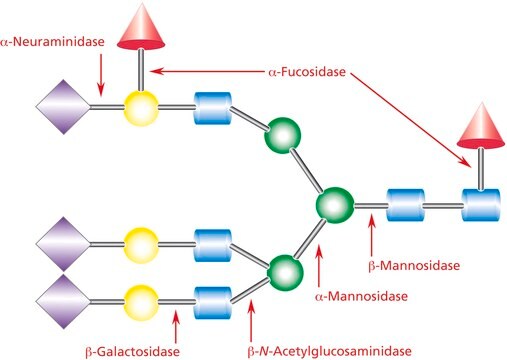
N7885
Neuraminidase from Vibrio cholerae
Type III, buffered aqueous solution, 0.2 μm filtered, 1-5 units/mg protein (Lowry, using NAN-lactose)
Synonyme(s) :
Acyl-neuraminyl Hydrolase, Receptor-destroying enzyme, Sialidase
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Type
Type III
Forme
buffered aqueous solution
Activité spécifique
1-5 units/mg protein (Lowry, using NAN-lactose)
Poids mol.
83 kDa
Application(s)
diagnostic assay manufacturing
Activité étrangère
Protease and NAN-aldolase, present
Température de stockage
2-8°C
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Catégories apparentées
Description générale
Application
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Qualité
Définition de l'unité
Forme physique
Notes préparatoires
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Resp. Sens. 1
Code de la classe de stockage
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 1
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Vous ne trouvez pas la bonne version ?
Si vous avez besoin d'une version particulière, vous pouvez rechercher un certificat spécifique par le numéro de lot.
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Protocoles
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique