MSP08
Membrane Scaffold Protein 1E3D1
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, buffered aqueous solution
Synonyme(s) :
Membrane Scaffold Protein 1E3D1, MSP1E3D1
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Produit recombinant
expressed in E. coli
Niveau de qualité
Pureté
≥90% (SDS-GE)
Forme
buffered aqueous solution
Poids mol.
32,599.6 Da
Solubilité
water: soluble
Conditions d'expédition
ambient
Température de stockage
−20°C
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
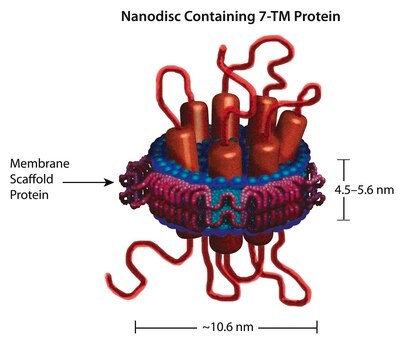
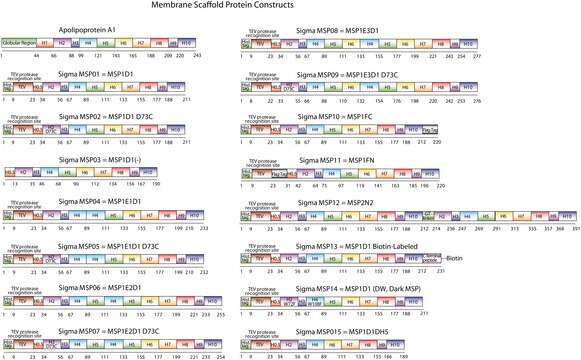
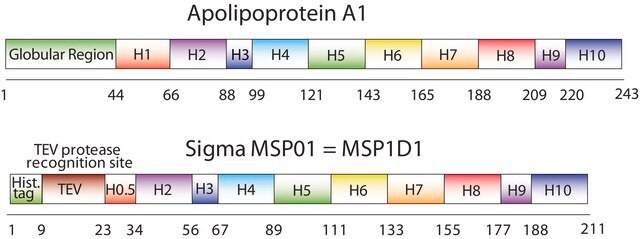
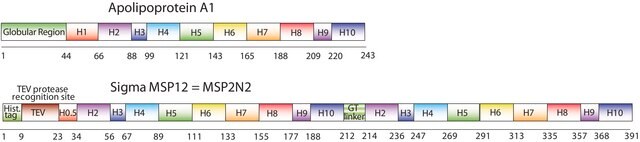
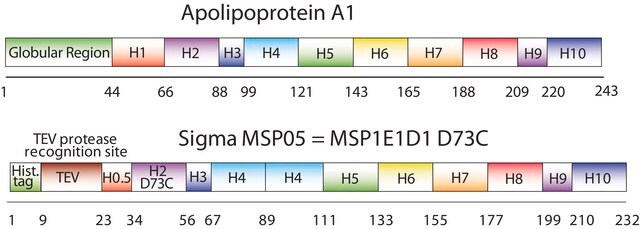
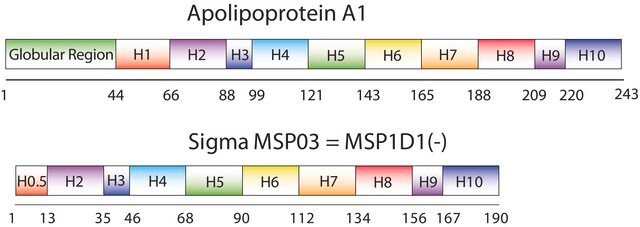
Nanodiscs are non-covalent structures that contain a phospholipid bilayer and a membrane scaffold protein (MSP), a genetically engineered protein, which mimics the function of Apolipoprotein A-1 (ApoA-1). The first MSP, MSP1, was engineered with its sequence based on the sequence of A-1, but without the globular N-terminal domain of native A-1. The MSP1E3D1 variant of MSP1 differs from MSP1 in the following facets: It deletes the first 11 amino acids in the Helix 1 portion (referred to as “H0.5” in the accompanying figure) of the original MSP1 sequence3 (which is known separately as MSP1D1). It repeats the Helix 4 (H4), Helix 5 (H5) and Helix 6 (H6) sequences of the original MSP1 sequence between the parent Helix 6 (H6) and Helix 7 (H7) segments of MSP1D1.
Application
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Informations légales
- 7,691,414 Membrane scaffold proteins
- 7,662,410 Membrane scaffold proteins and embedded membrane proteins
- 7,622,437 Tissue factor compositions and methods
- 7,592,008 Membrane scaffold proteins
- 7,575,763 Membrane scaffold proteins and tethered membrane proteins
- 7,083,958 Membrane scaffold proteins
- 7,048,949 Membrane scaffold proteins
- 7,691,414 Membrane scaffold proteins
- 7,662,410 Membrane scaffold proteins and embedded membrane proteins
- 7,622,437 Tissue factor compositions and methods
- 7,592,008 Membrane scaffold proteins
- 7,575,763 Membrane scaffold proteins and tethered membrane proteins
- 7,083,958 Membrane scaffold proteins
- 7,048,949 Membrane scaffold proteins
Code de la classe de stockage
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 2
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Protocoles
Protocols for Membrane Scaffold Proteins and Nanodisc Formation
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique