L7260
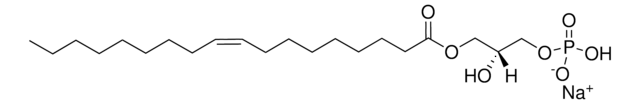
Oleoyl-L-α-lysophosphatidic acid sodium salt
≥98%, solid
Synonyme(s) :
1-Oleoyl-sn-glycerol 3-phosphate sodium salt, 3-sn-Lysophosphatidic acid, 1-oleoyl sodium salt, LPA sodium salt
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Pureté
≥98%
Forme
solid
Couleur
white
Type de lipide
phosphoglycerides
Température de stockage
−20°C
Chaîne SMILES
O[C@](COP([O-])(O)=O)([H])COC(CCCCCCC/C=C\CCCCCCCC)=O.[Na+]
InChI
1S/C21H41O7P.Na.H/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-21(23)27-18-20(22)19-28-29(24,25)26;;/h9-10,20,22H,2-8,11-19H2,1H3,(H2,24,25,26);;/b10-9+;;
Clé InChI
CHJOEWDRTPWOCY-TTWKNDKESA-N
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Application
- for the activation of Ras homolog gene family, member A (RhoA) and expression of claudin-1 in human breast cancer epithelial cell line
- in RH7777 cells for cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) accumulation assay and calcium mobilisation assay
- in vitro luciferase assay and live-cell imaging
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Caractéristiques et avantages
Attention
Notes préparatoires
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique